Massachusetts (
Massachusett
The Massachusett were a Native American tribe from the region in and around present-day Greater Boston in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. The name comes from the Massachusett language term for "At the Great Hill," referring to the Blue Hills ...
: ''Muhsachuweesut
məhswatʃəwiːsət">Massachusett writing systems">məhswatʃəwiːsət'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous
state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
in the
New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
region of the
Northeastern United States
The Northeastern United States, also referred to as the Northeast, the East Coast, or the American Northeast, is a geographic region of the United States. It is located on the Atlantic coast of North America, with Canada to its north, the Southe ...
. It borders on the
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
and
Gulf of Maine
The Gulf of Maine is a large gulf of the Atlantic Ocean on the east coast of North America. It is bounded by Cape Cod at the eastern tip of Massachusetts in the southwest and by Cape Sable Island at the southern tip of Nova Scotia in the northeast ...
to the east,
Connecticut
Connecticut () is the southernmost state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. Its cap ...
and
Rhode Island
Rhode Island (, like ''road'') is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is the List of U.S. states by area, smallest U.S. state by area and the List of states and territories of the United States ...
to the south,
New Hampshire
New Hampshire is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. It is bordered by Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ...
and
Vermont
Vermont () is a state in the northeast New England region of the United States. Vermont is bordered by the states of Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, and New York to the west, and the Canadian province of Quebec to ...
to the north, and
New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
to the west. The state's capital and
most populous city
The United Nations uses three definitions for what constitutes a city, as not all cities in all jurisdictions are classified using the same criteria. Cities may be defined as the city proper, cities proper, the extent of their urban area, or th ...
, as well as its cultural and
financial center
A financial centre ( BE), financial center ( AE), or financial hub, is a location with a concentration of participants in banking, asset management, insurance or financial markets with venues and supporting services for these activities to t ...
, is
Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
. Massachusetts is also home to the
urban
Urban means "related to a city". In that sense, the term may refer to:
* Urban area, geographical area distinct from rural areas
* Urban culture, the culture of towns and cities
Urban may also refer to:
General
* Urban (name), a list of people ...
core of
Greater Boston
Greater Boston is the metropolitan region of New England encompassing the municipality of Boston (the capital of the U.S. state of Massachusetts and the most populous city in New England) and its surrounding areas. The region forms the northern ar ...
, the largest metropolitan area in New England and a region profoundly influential upon American
history
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the History of writing#Inventions of writing, invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbr ...
,
academia
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of secondary education, secondary or tertiary education, tertiary higher education, higher learning (and generally also research or honorary membershi ...
, and the
research economy.
Originally dependent on
agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
,
fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment, but may also be caught from stocked bodies of water such as ponds, canals, park wetlands and reservoirs. Fishing techniques inclu ...
, and
trade
Trade involves the transfer of goods and services from one person or entity to another, often in exchange for money. Economists refer to a system or network that allows trade as a market.
An early form of trade, barter, saw the direct excha ...
. Massachusetts was transformed into a manufacturing center during the
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
. During the 20th century, Massachusetts's economy
shifted from manufacturing to services. Modern Massachusetts is a global leader in
biotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used b ...
,
engineering
Engineering is the use of scientific method, scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad rang ...
,
higher education
Higher education is tertiary education leading to award of an academic degree. Higher education, also called post-secondary education, third-level or tertiary education, is an optional final stage of formal learning that occurs after completi ...
,
finance
Finance is the study and discipline of money, currency and capital assets. It is related to, but not synonymous with economics, the study of production, distribution, and consumption of money, assets, goods and services (the discipline of fina ...
, and
maritime trade
Maritime may refer to:
Geography
* Maritime Alps, a mountain range in the southwestern part of the Alps
* Maritime Region, a region in Togo
* Maritime Southeast Asia
* The Maritimes, the Canadian provinces of Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, and Princ ...
.
Massachusetts was a site of early English colonization:
the Plymouth Colony was founded in 1620 by the
Pilgrims of the ''
Mayflower
''Mayflower'' was an English ship that transported a group of English families, known today as the Pilgrims, from England to the New World in 1620. After a grueling 10 weeks at sea, ''Mayflower'', with 102 passengers and a crew of about 30, r ...
'', and in 1630 the
Massachusetts Bay Colony
The Massachusetts Bay Colony (1630–1691), more formally the Colony of Massachusetts Bay, was an English settlement on the east coast of North America around the Massachusetts Bay, the northernmost of the several colonies later reorganized as the ...
, taking its name from the indigenous
Massachusett people
The Massachusett were a Native American tribe from the region in and around present-day Greater Boston in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. The name comes from the Massachusett language term for "At the Great Hill," referring to the Blue Hills ...
, established settlements in Boston and Salem. In 1692, the town of
Salem
Salem may refer to: Places
Canada
Ontario
* Bruce County
** Salem, Arran–Elderslie, Ontario, in the municipality of Arran–Elderslie
** Salem, South Bruce, Ontario, in the municipality of South Bruce
* Salem, Dufferin County, Ontario, part ...
and surrounding areas experienced one of America's most infamous cases of
mass hysteria
Mass psychogenic illness (MPI), also called mass sociogenic illness, mass psychogenic disorder, epidemic hysteria, or mass hysteria, involves the spread of illness symptoms through a population where there is no infectious agent responsible for c ...
, the
Salem witch trials
The Salem witch trials were a series of hearings and prosecutions of people accused of witchcraft in colonial Massachusetts between February 1692 and May 1693. More than 200 people were accused. Thirty people were found guilty, 19 of whom w ...
. In 1777, General
Henry Knox
Henry Knox (July 25, 1750 – October 25, 1806), a Founding Father of the United States, was a senior general of the Continental Army during the Revolutionary War, serving as chief of artillery in most of Washington's campaigns. Following the ...
founded the
Springfield Armory
The Springfield Armory, more formally known as the United States Armory and Arsenal at Springfield located in the city of Springfield, Massachusetts, was the primary center for the manufacture of United States military firearms from 1777 until ...
, which, during the
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
, catalyzed numerous important technological advances, including
interchangeable parts
Interchangeable parts are parts ( components) that are identical for practical purposes. They are made to specifications that ensure that they are so nearly identical that they will fit into any assembly of the same type. One such part can freely r ...
. In 1786,
Shays' Rebellion
Shays Rebellion was an armed uprising in Western Massachusetts and Worcester in response to a debt crisis among the citizenry and in opposition to the state government's increased efforts to collect taxes both on individuals and their trades. The ...
, a populist revolt led by disaffected
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
veterans, influenced the
United States Constitutional Convention
The Constitutional Convention took place in Philadelphia from May 25 to September 17, 1787. Although the convention was intended to revise the league of states and first system of government under the Articles of Confederation, the intention fr ...
.
In the 18th century, the Protestant
First Great Awakening
The First Great Awakening (sometimes Great Awakening) or the Evangelical Revival was a series of Christian revivals that swept Britain and its thirteen North American colonies in the 1730s and 1740s. The revival movement permanently affecte ...
, which swept Britain and the
Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies, the Thirteen American Colonies, or later as the United Colonies, were a group of Kingdom of Great Britain, British Colony, colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Fo ...
, originated from the pulpit of
Northampton
Northampton () is a market town and civil parish in the East Midlands of England, on the River Nene, north-west of London and south-east of Birmingham. The county town of Northamptonshire, Northampton is one of the largest towns in England; ...
preacher
Jonathan Edwards Jonathan Edwards may refer to:
Musicians
*Jonathan and Darlene Edwards, pseudonym of bandleader Paul Weston and his wife, singer Jo Stafford
*Jonathan Edwards (musician) (born 1946), American musician
** ''Jonathan Edwards'' (album), debut album ...
. In the late 18th century, Boston became known as the "Cradle of Liberty" for the agitation there that later led to the
American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolut ...
.
Massachusetts has played a powerful scientific, commercial, and cultural role in the history of the United States. Before the
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
, Massachusetts was a center for the
abolitionist
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people.
The British ...
,
temperance
Temperance may refer to:
Moderation
*Temperance movement, movement to reduce the amount of alcohol consumed
*Temperance (virtue), habitual moderation in the indulgence of a natural appetite or passion
Culture
*Temperance (group), Canadian danc ...
, and
transcendentalist movements. In the late 19th century, the sports of
basketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams, most commonly of five players each, opposing one another on a rectangular Basketball court, court, compete with the primary objective of #Shooting, shooting a basketball (ball), basketball (appr ...
and
volleyball
Volleyball is a team sport in which two teams of six players are separated by a net. Each team tries to score points by grounding a ball on the other team's court under organized rules. It has been a part of the official program of the Summ ...
were invented in the western Massachusetts cities of
Springfield
Springfield may refer to:
* Springfield (toponym), the place name in general
Places and locations Australia
* Springfield, New South Wales (Central Coast)
* Springfield, New South Wales (Snowy Monaro Regional Council)
* Springfield, Queenslan ...
and
Holyoke
Holyoke is a city in Hampden County, Massachusetts, United States, that lies between the western bank of the Connecticut River and the Mount Tom Range. As of the 2020 census, the city had a population of 38,238. Located north of Springfield ...
, respectively.
Massachusetts became the first U.S. state to legally recognize
same-sex marriage
Same-sex marriage, also known as gay marriage, is the marriage of two people of the same Legal sex and gender, sex or gender. marriage between same-sex couples is legally performed and recognized in 33 countries, with the most recent being ...
as a result of the
Massachusetts Supreme Judicial Court
The Massachusetts Supreme Judicial Court (SJC) is the court of last resort, highest court in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts. Although the claim is disputed by the Supreme Court of Pennsylvania, the SJC claims the di ...
's decision in ''
Goodridge v. Department of Public Health
''Goodridge v. Dept. of Public Health'', 798 N.E.2d 941 ( Mass. 2003), is a landmark Massachusetts Supreme Judicial Court case in which the Court held that the Massachusetts Constitution requires the state to legally recognize same-sex marria ...
'' in 2004,
and elected the first openly
lesbian
A lesbian is a Homosexuality, homosexual woman.Zimmerman, p. 453. The word is also used for women in relation to their sexual identity or sexual behavior, regardless of sexual orientation, or as an adjective to characterize or associate n ...
U.S. state governor in 2022, by a wide margin—and Boston is a hub of
LGBT culture
LGBT culture is a culture shared by lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer individuals. It is sometimes referred to as queer culture (indicating people who are queer), while the term gay culture may be used to mean "LGBT culture" o ...
and
LGBT activism
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) movements are social movements that advocate for LGBT people in society. Some focus on equal rights, such as the ongoing movement for same-sex marriage, while others focus on liberation, as in the ...
in the United States. Prominent American political dynasties have hailed from the state, including the
Adams and
Kennedy
Kennedy may refer to:
People
* John F. Kennedy (1917–1963), 35th president of the United States
* John Kennedy (Louisiana politician), (born 1951), US Senator from Louisiana
* Kennedy (surname), a family name (including a list of persons with t ...
families.
Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher le ...
in
Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge bec ...
is the
oldest institution of higher learning in the United States, with the largest
financial endowment
A financial endowment is a legal structure for managing, and in many cases indefinitely perpetuating, a pool of financial, real estate, or other investments for a specific purpose according to the will of its founders and donors. Endowments are o ...
of any university. The university has educated
eight
8 is a number, numeral, and glyph.
8 or eight may also refer to:
Years
* AD 8, the eighth year of the AD era
* 8 BC, the eighth year before the AD era
Art
*The Eight (Ashcan School), a group of twentieth century painters associated with the As ...
Presidents of the United States
The president of the United States is the head of state and head of government of the United States, indirectly elected to a four-year term via the Electoral College. The officeholder leads the executive branch of the federal government and ...
while
Harvard Law School
Harvard Law School (Harvard Law or HLS) is the law school of Harvard University, a private research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1817, it is the oldest continuously operating law school in the United States.
Each class ...
has educated a contemporaneous majority of Justices of the
Supreme Court of the United States
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that involve a point o ...
.
Kendall Square
Kendall Square is a neighborhood in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The square itself at the intersection of Main Street and Broadway. It also refers to the broad business district east of Portland Street, northwest of the Charles River, north of MIT ...
in
Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge bec ...
has been called "the most innovative square mile on the planet", in reference to the high concentration of
entrepreneurial
Entrepreneurship is the creation or extraction of economic value. With this definition, entrepreneurship is viewed as change, generally entailing risk beyond what is normally encountered in starting a business, which may include other values th ...
start-ups
A startup or start-up is a company or project undertaken by an entrepreneur to seek, develop, and validate a scalable business model. While entrepreneurship refers to all new businesses, including self-employment and businesses that never intend t ...
and quality of
innovation
Innovation is the practical implementation of ideas that result in the introduction of new goods or services or improvement in offering goods or services. ISO TC 279 in the standard ISO 56000:2020 defines innovation as "a new or changed entity ...
which have emerged in the vicinity of the square since 2010. Both
Harvard
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher le ...
and
MIT
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern technology and science, and is one of the mo ...
, also in
Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge bec ...
, are perennially ranked as either the most or among the most highly regarded
academic institution
Academic institution is an educational institution dedicated to education and research, which grants academic degrees. See also academy and university.
Types
* Primary schools – (from French ''école primaire'') institutions where children r ...
s in the world.
''Times Higher Education''. Accessed December 3, 2016. The state's public-school students place among the top tier in the world in academic performance.
Massachusetts has been ranked as one of the top states in the United States for citizens to live in, as well as one of the most expensive.
Massachusetts is one of the most educated, developed, and wealthiest states, ranking List of U.S. states and territories by educational attainment, 1st in percentage of population 25 and over with a bachelor's degree and 1st in percentage of population 25 and over with an advanced degree, List of U.S. states by American Human Development Index, 1st on the American Human Development Index, List of U.S. states and territories by income, 1st in per capita income and 2nd in median household income.
Etymology
The
Massachusetts Bay Colony
The Massachusetts Bay Colony (1630–1691), more formally the Colony of Massachusetts Bay, was an English settlement on the east coast of North America around the Massachusetts Bay, the northernmost of the several colonies later reorganized as the ...
was named after the
indigenous peoples, indigenous population, the
Massachusett
The Massachusett were a Native American tribe from the region in and around present-day Greater Boston in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. The name comes from the Massachusett language term for "At the Great Hill," referring to the Blue Hills ...
, whose name likely derived from a
Wôpanâak word ''muswachasut'', segmented as ''mus(ây)'' "big" + ''wach'' "mountain" + ''-s'' "diminutive" + -''ut'' "locative". It has been translated as "near the great hill", "by the blue hills", "at the little big hill", or "at the range of hills." This in reference to the
Blue Hills—namely, the
Great Blue Hill
Great Blue Hill is a hill of 635 feet (194 m) located within the Blue Hills Reservation in Milton, Randolph and Canton, Massachusetts, about south of downtown Boston. It is the highest point in Norfolk County and the Greater Boston area.
The ...
, which is located on the boundary of
Milton
Milton may refer to:
Names
* Milton (surname), a surname (and list of people with that surname)
** John Milton (1608–1674), English poet
* Milton (given name)
** Milton Friedman (1912–2006), Nobel laureate in Economics, author of '' Free t ...
and
Canton
Canton may refer to:
Administrative division terminology
* Canton (administrative division), territorial/administrative division in some countries, notably Switzerland
* Township (Canada), known as ''canton'' in Canadian French
Arts and ent ...
. ''Massachusett'' has also been represented as ''Moswetuset.'' This comes from the name of the
Moswetuset Hummock
Moswetuset Hummock is a Native American site and the original name of the tribe (Mosetuset) in the region named Massachusetts after them. The wooded hummock in Squantum, Massachusetts, is formally recognized as historic by descendants of the Ponk ...
(meaning "hill shaped like an arrowhead") in
Quincy, where
Plymouth Colony
Plymouth Colony (sometimes Plimouth) was, from 1620 to 1691, the British America, first permanent English colony in New England and the second permanent English colony in North America, after the Jamestown Colony. It was first settled by the pa ...
commander
Myles Standish
Myles Standish (c. 1584 – October 3, 1656) was an English military officer and colonizer. He was hired as military adviser for Plymouth Colony in present-day Massachusetts, United States by the Pilgrims. Standish accompanied the Pilgrims on ...
(a hired English military officer) and
Squanto
Tisquantum (; 1585 (±10 years?) – late November 1622 O.S.), more commonly known as Squanto Sam (), was a member of the Patuxet tribe best known for being an early liaison between the Native American population in Southern New England and t ...
(a member of the
Patuxet band of the
Wamponoag people, who have since died off due to contagious disease brought by colonizers) met Chief
Chickatawbut
Chickatawbut (died 1633; also known as Cicatabut and possibly as Oktabiest before 1622) was the sachem, or leader, of a large group of indigenous people known as the Massachusett tribe in what is now eastern Massachusetts, United States, during th ...
in 1621.
While the designation "Commonwealth" forms part of the state's official name, in modern times it has no practical implications and Massachusetts has the same position and powers within the United States as other states.
John Adams
John Adams (October 30, 1735 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, attorney, diplomat, writer, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the second president of the United States from 1797 to 1801. Befor ...
may have chosen the word in 1779 for the second draft of what became the 1780
Massachusetts Constitution
The Constitution of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts is the fundamental governing document of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, one of the 50 individual state governments that make up the United States of America. As a member of the Massachuset ...
; unlike the "state", the word "commonwealth" had the connotation of a
republic
A republic () is a "state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th c ...
at the time. This was in contrast to the
monarchy
A monarchy is a form of government in which a person, the monarch, is head of state for life or until abdication. The political legitimacy and authority of the monarch may vary from restricted and largely symbolic (constitutional monarchy) ...
the former
American colonies were fighting against. (The name "State of Massachusetts Bay" appeared in the first draft, which was ultimately rejected.) It was also chosen to include the "Cape Islands" in reference to
Martha's Vineyard
Martha's Vineyard, often simply called the Vineyard, is an island in the Northeastern United States, located south of Cape Cod in Dukes County, Massachusetts, known for being a popular, affluent summer colony. Martha's Vineyard includes the s ...
and
Nantucket
Nantucket () is an island about south from Cape Cod. Together with the small islands of Tuckernuck and Muskeget, it constitutes the Town and County of Nantucket, a combined county/town government that is part of the U.S. state of Massachuse ...
—from 1780 to 1844, they were seen as additional and separate entities confined within the Commonwealth.
History
Pre-colonization
Massachusetts was originally inhabited by tribes of the
Algonquian language family
The Algonquian languages ( or ; also Algonkian) are a subfamily of indigenous American languages that include most languages in the Algic language family. The name of the Algonquian language family is distinguished from the orthographically simi ...
, including:
Wampanoag
The Wampanoag , also rendered Wôpanâak, are an Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands based in southeastern Massachusetts and historically parts of eastern Rhode Island,Salwen, "Indians of Southern New England and Long Island," p. 17 ...
,
Narragansett,
Nipmuc
The Nipmuc or Nipmuck people are an Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands, who historically spoke an Eastern Algonquian language. Their historic territory Nippenet, "the freshwater pond place," is in central Massachusetts and nearby part ...
,
Pocomtuc
The Pocumtuc (also Pocomtuck or Deerfield Indians) were a Native American tribe historically inhabiting western areas of Massachusetts.
Settlements
Their territory was concentrated around the confluence of the Deerfield and Connecticut Rivers ...
,
Mahican
The Mohican ( or , alternate spelling: Mahican) are an Eastern Algonquian Native American tribe that historically spoke an Algonquian language. As part of the Eastern Algonquian family of tribes, they are related to the neighboring Lenape, who ...
, and
Massachusett
The Massachusett were a Native American tribe from the region in and around present-day Greater Boston in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. The name comes from the Massachusett language term for "At the Great Hill," referring to the Blue Hills ...
.
While cultivation of crops like
squash
Squash may refer to:
Sports
* Squash (sport), the high-speed racquet sport also known as squash racquets
* Squash (professional wrestling), an extremely one-sided match in professional wrestling
* Squash tennis, a game similar to squash but pla ...
and
corn
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. Th ...
were an important part of their diet, the people of these tribes hunted, fished, and searched the forest for most of their food. Villagars lived in lodges called
wigwam
A wigwam, wickiup, wetu (Wampanoag), or wiigiwaam (Ojibwe, in syllabics: ) is a semi-permanent domed dwelling formerly used by certain Native American tribes and First Nations people and still used for ceremonial events. The term ''wickiup'' ...
s as well as
longhouse
A longhouse or long house is a type of long, proportionately narrow, single-room building for communal dwelling. It has been built in various parts of the world including Asia, Europe, and North America.
Many were built from timber and often rep ...
s.
Tribes were led by male or female elders known as
sachem
Sachems and sagamores are paramount chiefs among the Algonquians or other Native American tribes of northeastern North America, including the Iroquois. The two words are anglicizations of cognate terms (c. 1622) from different Eastern Al ...
s.
Colonial period
In the early 1600s,
European colonizers caused
virgin soil epidemic
Virgin soil epidemic is a term coined by Alfred Crosby, who defined it as epidemics "in which the populations at risk have had no previous contact with the diseases that strike them and are therefore immunologically almost defenseless." His conc ...
s such as
smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) c ...
,
measles
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than , cough, ...
,
influenza
Influenza, commonly known as "the flu", is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These symptoms ...
, and perhaps
leptospirosis
Leptospirosis is a blood infection caused by the bacteria ''Leptospira''. Signs and symptoms can range from none to mild (headaches, muscle pains, and fevers) to severe ( bleeding in the lungs or meningitis). Weil's disease, the acute, severe ...
in what is now known as the
northeastern region of the United States. Between 1617 and 1619, what was most likely smallpox killed approximately 90% of the
Massachusetts Bay
Massachusetts Bay is a bay on the Gulf of Maine that forms part of the central coastline of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts.
Description
The bay extends from Cape Ann on the north to Plymouth Harbor on the south, a distance of about . Its ...
Native Americans.

The first English colonizers in Massachusetts, the
Puritans
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to purify the Church of England of Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should become more Protestant. P ...
, arrived on the ''
Mayflower
''Mayflower'' was an English ship that transported a group of English families, known today as the Pilgrims, from England to the New World in 1620. After a grueling 10 weeks at sea, ''Mayflower'', with 102 passengers and a crew of about 30, r ...
'' at
Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west.
Plymouth ...
in 1620. This was the second permanent
English colony in the part of North America that later became the United States, after the
Jamestown Colony
The Jamestown settlement in the Colony of Virginia was the first permanent English settlement
''English Settlement'' is the fifth studio album and first double album by the English rock band XTC, released 12 February 1982 on Virgin Reco ...
. The
"First Thanksgiving" was celebrated by the Puritans after their first harvest in the "
New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. 3 ...
" and lasted for three days. They were soon followed by other Puritans, who colonized the
Massachusetts Bay Colony
The Massachusetts Bay Colony (1630–1691), more formally the Colony of Massachusetts Bay, was an English settlement on the east coast of North America around the Massachusetts Bay, the northernmost of the several colonies later reorganized as the ...
—now known as Boston—in 1630.
The Puritans believed the
Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Britain ...
needed to be purified and experienced harassment due to being disliked by English authority.
They decided to colonize to Massachusetts intending to establish what they considered an "ideal" religious society. Unlike the Plymouth colony, the
Massachusetts Bay Colony
The Massachusetts Bay Colony (1630–1691), more formally the Colony of Massachusetts Bay, was an English settlement on the east coast of North America around the Massachusetts Bay, the northernmost of the several colonies later reorganized as the ...
was colonized under a royal charter in 1629. Both religious dissent and expansionism resulted in several new colonies being founded, shortly after Plymouth and Massachusetts Bay, elsewhere in New England. The Massachusetts Bay banished dissenters such as
Anne Hutchinson
Anne Hutchinson (née Marbury; July 1591 – August 1643) was a Puritan spiritual advisor, religious reformer, and an important participant in the Antinomian Controversy which shook the infant Massachusetts Bay Colony from 1636 to 1638. Her ...
and
Roger Williams
Roger Williams (21 September 1603between 27 January and 15 March 1683) was an English-born New England Puritan minister, theologian, and author who founded Providence Plantations, which became the Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantation ...
due to religious and political conflict. In 1636, Williams colonized what is now known as
Rhode Island
Rhode Island (, like ''road'') is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is the List of U.S. states by area, smallest U.S. state by area and the List of states and territories of the United States ...
, and Hutchinson joined him there several years later. Religious intolerance continued, and among those who objected to this later in the century were the English Quaker preachers
Alice and Thomas Curwen, who were publicly flogged and imprisoned in Boston in 1676.
In 1641, Massachusetts expanded inland significantly. The Commonwealth acquired the
Connecticut River Valley
The Connecticut River is the longest river in the New England region of the United States, flowing roughly southward for through four states. It rises 300 yards (270 m) south of the U.S. border with Quebec, Canada, and discharges at Long Island ...
settlement of
Springfield
Springfield may refer to:
* Springfield (toponym), the place name in general
Places and locations Australia
* Springfield, New South Wales (Central Coast)
* Springfield, New South Wales (Snowy Monaro Regional Council)
* Springfield, Queenslan ...
, which had recently disputed with—and defected from—its original administrators, the
Connecticut Colony
The ''Connecticut Colony'' or ''Colony of Connecticut'', originally known as the Connecticut River Colony or simply the River Colony, was an English colony in New England which later became Connecticut. It was organized on March 3, 1636 as a settl ...
. This established Massachusetts's southern border in the west, though this became
disputed territory
A territorial dispute or boundary dispute is a disagreement over the possession or control of land between two or more political entities.
Context and definitions
Territorial disputes are often related to the possession of natural resources su ...
until 1803–04 due to surveying problems.
Currency was another issue in the colonies. In 1652 the
Massachusetts legislature
The Massachusetts General Court (formally styled the General Court of Massachusetts) is the state legislature of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. The name "General Court" is a hold-over from the earliest days of the Massachusetts Bay Colony, w ...
authorized
John Hull to produce coinage (
mintmaster). "The Hull Mint produced several denominations of silver coinage, including
the pine tree shilling
The pine tree shilling was a type of coin minted and circulated in the thirteen colonies.
The Massachusetts Bay Colony established a mint in Boston in 1652. John Hull was Treasurer and mintmaster; Hull's partner at the "Hull Mint" was Robert S ...
, for over 30 years until the political and economic situation made operating the mint no longer practical." Mostly political for
Charles II of England deemed the "Hull Mint"
high treason in the United Kingdom
Under the law of the United Kingdom, high treason is the crime of disloyalty to the Crown. Offences constituting high treason include plotting the murder of the sovereign; committing adultery with the sovereign's consort, with the sovereign's eld ...
which had a punishment of
Hanging, drawing and quartering
To be hanged, drawn and quartered became a statutory penalty for men convicted of high treason in the Kingdom of England from 1352 under King Edward III (1327–1377), although similar rituals are recorded during the reign of King Henry III ( ...
. "On April 6, 1681, Randolph petitioned the king, informing him the colony was still pressing their own coins which he saw as high treason and believed it was enough to void the charter. He asked that a writ of Quo warranto (a legal action requiring the defendant to show what authority they have for exercising some right, power, or franchise they claim to hold) be issued against Massachusetts for the violations."
In 1691, the colonies of Massachusetts Bay and Plymouth were united (along with present-day
Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and north ...
, which had previously been divided between Massachusetts and
New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
) into the
Province of Massachusetts Bay
The Province of Massachusetts Bay was a colony in British America which became one of the Thirteen Colonies, thirteen original states of the United States. It was chartered on October 7, 1691, by William III of England, William III and Mary II ...
. Shortly after the arrival of the new province's first governor,
William Phips
Sir William Phips (or Phipps; February 2, 1651 – February 18, 1695) was born in Maine in the Massachusetts Bay Colony and was of humble origin, uneducated, and fatherless from a young age but rapidly advanced from shepherd boy, to shipwright, s ...
, the
Salem witch trials
The Salem witch trials were a series of hearings and prosecutions of people accused of witchcraft in colonial Massachusetts between February 1692 and May 1693. More than 200 people were accused. Thirty people were found guilty, 19 of whom w ...
took place, where a number of men and women were hanged for alleged
witchcraft
Witchcraft traditionally means the use of magic or supernatural powers to harm others. A practitioner is a witch. In medieval and early modern Europe, where the term originated, accused witches were usually women who were believed to have us ...
.
The
most destructive earthquake yet known in
New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
occurred in 1755, causing considerable damage across Massachusetts.
The Revolutionary War

Massachusetts was a center of the movement for independence from
Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
; colonists in Massachusetts had long uneasy relations with the British monarchy, including open rebellion under the
Dominion of New England
The Dominion of New England in America (1686–1689) was an administrative union of English colonies covering New England and the Mid-Atlantic Colonies (except for Delaware Colony and the Province of Pennsylvania). Its political structure represe ...
in the 1680s. Protests against British attempts to tax the colonies after the
French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the ...
ended in 1763 led to the
Boston Massacre
The Boston Massacre (known in Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain as the Incident on King Street) was a confrontation in Boston on March 5, 1770, in which a group of nine British soldiers shot five people out of a crowd of three or four hu ...
in 1770, and the 1773
Boston Tea Party
The Boston Tea Party was an American political and mercantile protest by the Sons of Liberty in Boston, Massachusetts, on December 16, 1773. The target was the Tea Act of May 10, 1773, which allowed the British East India Company to sell tea ...
escalated tensions. In 1774, the
Intolerable Acts
The Intolerable Acts were a series of punitive laws passed by the British Parliament in 1774 after the Boston Tea Party. The laws aimed to punish Massachusetts colonists for their defiance in the Tea Party protest of the Tea Act, a tax measure ...
targeted Massachusetts with punishments for the Boston Tea Party and further decreased local autonomy, increasing local dissent. Anti-Parliamentary activity by men such as
Samuel Adams
Samuel Adams ( – October 2, 1803) was an American statesman, political philosopher, and a Founding Father of the United States. He was a politician in colonial Massachusetts, a leader of the movement that became the American Revolution, and ...
and
John Hancock
John Hancock ( – October 8, 1793) was an American Founding Father, merchant, statesman, and prominent Patriot of the American Revolution. He served as president of the Second Continental Congress and was the first and third Governor of the ...
, followed by reprisals by the British government, were a primary reason for the unity of the
Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies, the Thirteen American Colonies, or later as the United Colonies, were a group of Kingdom of Great Britain, British Colony, colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Fo ...
and the outbreak of the
American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolut ...
in 1775.
The
Battles of Lexington and Concord
The Battles of Lexington and Concord were the first military engagements of the American Revolutionary War. The battles were fought on April 19, 1775, in Middlesex County, Province of Massachusetts Bay, within the towns of Lexington, Concord ...
initiated the
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
and were fought in the eponymous Massachusetts towns. Future President
George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of th ...
took over what would become the
Continental Army
The Continental Army was the army of the United Colonies (the Thirteen Colonies) in the Revolutionary-era United States. It was formed by the Second Continental Congress after the outbreak of the American Revolutionary War, and was establis ...
after the battle. His first victory was the
Siege of Boston
The siege of Boston (April 19, 1775 – March 17, 1776) was the opening phase of the American Revolutionary War. New England militiamen prevented the movement by land of the British Army, which was garrisoned in what was then the peninsular town ...
in the winter of 1775–76, after which the British were forced to evacuate the city. The event is still celebrated in
Suffolk County as
Evacuation Day. On the coast, Salem became a center for
privateer
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or deleg ...
ing. Although the documentation is incomplete, about 1,700
letters of marque, issued on a per-voyage basis, were granted during the American Revolution. Nearly 800 vessels were commissioned as privateers and are credited with capturing or destroying about 600 British ships.
Federal period
Bostonian
John Adams
John Adams (October 30, 1735 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, attorney, diplomat, writer, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the second president of the United States from 1797 to 1801. Befor ...
, known as the "Atlas of Independence", was highly involved in both separation from Britain and the
Constitution of Massachusetts
The Constitution of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts is the fundamental governing document of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, one of the 50 individual state governments that make up the United States of America. As a member of the Massachuset ...
, which effectively (the
Elizabeth Freeman
Elizabeth Freeman ( 1744 December 28, 1829), also known as Bet, Mum Bett, or MumBet, was the first enslaved African American to file and win a freedom suit in Massachusetts. The Massachusetts Supreme Judicial Court ruling, in Freeman's favor, ...
and
Quock Walker
Quock Walker, also known as Kwaku or Quork Walker (1753 – ?), was an American slavery, slave who sued for and won his freedom in June 1781 in a case citing language in the new Massachusetts Constitution (1780) that declared all men to be born fr ...
cases as interpreted by
William Cushing
William Cushing (March 1, 1732 – September 13, 1810) was one of the original five associate justices of the United States Supreme Court; confirmed by the United States Senate on September 26, 1789, he served until his death. His Supreme Court ...
) made Massachusetts the first state to abolish slavery. David McCullough points out that an equally important feature was its placing for the first time the courts as a co-equal branch separate from the executive. (The
Constitution of Vermont
The Constitution of the State of Vermont is the fundamental body of law of the U.S. state of Vermont, describing and framing its government. It was adopted in 1793 following Vermont's admission to the Union in 1791 and is largely based upon the ...
, adopted in 1777, represented the first partial ban on slavery. Vermont became a state in 1791 but did not fully ban slavery until 1858 with the Vermont Personal Liberty Law. The
Pennsylvania Gradual Abolition Act of 1780 made
Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
the first state to abolish slavery by statute.) Later, Adams was active in early American foreign affairs and succeeded Washington as the second United States President. His son
John Quincy Adams
John Quincy Adams (; July 11, 1767 – February 23, 1848) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, and diarist who served as the sixth president of the United States, from 1825 to 1829. He previously served as the eighth United States S ...
, also from Massachusetts, would go on to become the sixth
United States President
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United State ...
.
From 1786 to 1787, an armed uprising, known as
Shays' Rebellion
Shays Rebellion was an armed uprising in Western Massachusetts and Worcester in response to a debt crisis among the citizenry and in opposition to the state government's increased efforts to collect taxes both on individuals and their trades. The ...
led by Revolutionary War veteran
Daniel Shays
Daniel Shays (August 1747 September 29, 1825) was an American soldier, revolutionary and farmer famous for allegedly leading Shays' Rebellion, a populist uprising against controversial debt collection and tax policies in Massachusetts in 1786� ...
wrought havoc throughout Massachusetts and ultimately attempted to seize the
Federal armory
Federal or foederal (archaic) may refer to:
Politics
General
*Federal monarchy, a federation of monarchies
*Federation, or ''Federal state'' (federal system), a type of government characterized by both a central (federal) government and states or ...
.
[ The rebellion was one of the major factors in the decision to draft a stronger national constitution to replace the ]Articles of Confederation
The Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union was an agreement among the 13 Colonies of the United States of America that served as its first frame of government. It was approved after much debate (between July 1776 and November 1777) by ...
.[ On February 6, 1788, Massachusetts became the sixth state to ratify the ]United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the Supremacy Clause, supreme law of the United States, United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, in 1789. Originally comprising seven ar ...
.
19th century
In 1820, Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and north ...
separated from Massachusetts and entered the Union as the 23rd state as a result of the ratification of the Missouri Compromise
The Missouri Compromise was a federal legislation of the United States that balanced desires of northern states to prevent expansion of slavery in the country with those of southern states to expand it. It admitted Missouri as a Slave states an ...
.
 During the 19th century, Massachusetts became a national leader in the American
During the 19th century, Massachusetts became a national leader in the American Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
, with factories around cities such as Lowell and Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
producing textiles and shoes, and factories around Springfield producing tools, paper, and textiles. The economy transformed from one based primarily on agriculture to an industrial one, initially making use of water-power and later the steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be trans ...
to power factories. Canals and railroads were used for transporting raw materials and finished goods. At first, the new industries drew labor from Yankee
The term ''Yankee'' and its contracted form ''Yank'' have several interrelated meanings, all referring to people from the United States. Its various senses depend on the context, and may refer to New Englanders, residents of the Northern United St ...
s on nearby subsistence farms, and later relied upon immigrant labor from Europe and Canada.
Although Massachusetts was the first slave-holding colony dating back to the early 1600s, in the years leading up to the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
, Massachusetts was a center of progressivist
Progressivism holds that it is possible to improve human societies through political action. As a political movement, progressivism seeks to advance the human condition through social reform based on purported advancements in science, techn ...
and abolitionist
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people.
The British ...
activity. Horace Mann
Horace Mann (May 4, 1796August 2, 1859) was an American educational reformer, slavery abolitionist and Whig politician known for his commitment to promoting public education. In 1848, after public service as Secretary of the Massachusetts Sta ...
made the state's school system a national model. Henry David Thoreau
Henry David Thoreau (July 12, 1817May 6, 1862) was an American naturalist, essayist, poet, and philosopher. A leading Transcendentalism, transcendentalist, he is best known for his book ''Walden'', a reflection upon simple living in natural su ...
and Ralph Waldo Emerson
Ralph Waldo Emerson (May 25, 1803April 27, 1882), who went by his middle name Waldo, was an American essayist, lecturer, philosopher, abolitionist, and poet who led the transcendentalist movement of the mid-19th century. He was seen as a champ ...
made major contributions to American philosophy. Members of the transcendentalist movement
Transcendentalism is a philosophical movement that developed in the late 1820s and 1830s in New England. "Transcendentalism is an American literary, political, and philosophical movement of the early nineteenth century, centered around Ralph Wald ...
emphasized the importance of the natural world and emotion to humanity.
Although significant opposition to abolitionism existed early on in Massachusetts, resulting in anti-abolitionist riots between 1835 and 1837, opposition to slavery gradually increased throughout the next few decades. Abolitionists John Brown John Brown most often refers to:
*John Brown (abolitionist) (1800–1859), American who led an anti-slavery raid in Harpers Ferry, Virginia in 1859
John Brown or Johnny Brown may also refer to:
Academia
* John Brown (educator) (1763–1842), Ir ...
and Sojourner Truth
Sojourner Truth (; born Isabella Baumfree; November 26, 1883) was an American abolitionist of New York Dutch heritage and a women's rights activist. Truth was born into slavery in Swartekill, New York, but escaped with her infant daughter to f ...
lived in Springfield and Northampton, respectively, while Frederick Douglass
Frederick Douglass (born Frederick Augustus Washington Bailey, February 1817 or 1818 – February 20, 1895) was an American social reformer, abolitionist, orator, writer, and statesman. After escaping from slavery in Maryland, he became ...
lived in Boston and Susan B. Anthony
Susan B. Anthony (born Susan Anthony; February 15, 1820 – March 13, 1906) was an American social reformer and women's rights activist who played a pivotal role in the women's suffrage movement. Born into a Quaker family committed to so ...
in Adams, Massachusetts. The works of such abolitionists contributed to Massachusetts's actions during the Civil War. Massachusetts was the first state to recruit, train, and arm a Black
Black is a color which results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without hue, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness. Black and white have o ...
regiment with White
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White on ...
officers, the 54th Massachusetts Infantry Regiment
The 54th Massachusetts Infantry Regiment was an infantry regiment that saw extensive service in the Union Army during the American Civil War. The unit was the second African-American regiment, following the 1st Kansas Colored Volunteer Infantry ...
. In 1852, Massachusetts became the first state to pass compulsory education
Compulsory education refers to a period of education that is required of all people and is imposed by the government. This education may take place at a registered school or at other places.
Compulsory school attendance or compulsory schooling ...
laws.
20th century
Although the American stock market had sustained steep losses the last week in October 1929, Tuesday, October 29 is remembered as the beginning of the Great Depression. The Boston Stock Exchange
The Boston Stock Exchange (now NASDAQ BX, formerly ''BSE'') is a regional stock exchange located in Boston, Massachusetts. It was founded in 1834, making it the third-oldest stock exchange in the United States. On October 2, 2007, NASDAQ agreed t ...
, drawn into the whirlpool of panic selling that beset the New York Stock Exchange, lost over 25 percent of its value in two days of frenzied trading. The BSE, nearly 100 years old at the time, had helped raise the capital that had funded many of the Commonwealth's factories, railroads, and businesses. " Governor of Massachusetts Frank G. Allen
Frank Gilman Allen (October 6, 1874October 9, 1950) was an American businessman and politician from Massachusetts. He was president of a successful leathergoods business in Norwood, Massachusetts, and active in local and state politics. A Repub ...
appointed John C. Hull the first Securities Director of Massachusetts.
Hull would assume office in January 1930. His term would end in 1936.
With the departure of several manufacturing companies, the area's industrial economy began to decline during the early 20th century. By the 1920s, competition from the South and Midwest, followed by the Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
, led to the collapse of the three main industries in Massachusetts: textiles, shoemaking, and precision mechanics. This decline would continue into the latter half of the century; between 1950 and 1979, the number of Massachusetts residents involved in textile manufacturing declined from 264,000 to 63,000. The 1969 closure of the Springfield Armory
The Springfield Armory, more formally known as the United States Armory and Arsenal at Springfield located in the city of Springfield, Massachusetts, was the primary center for the manufacture of United States military firearms from 1777 until ...
, in particular, spurred an exodus of high-paying jobs from Western Massachusetts, which suffered greatly as it de-industrialized during the last 40 years of the 20th century.
Massachusetts manufactured 3.4 percent of total United States military armaments produced during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, ranking tenth among the 48 states. In Eastern Massachusetts, following World WarII, the economy was transformed from one based on heavy industry into a service-based economy. Government contracts, private investment, and research facilities led to a new and improved industrial climate, with reduced unemployment and increased per capita income. Suburbanization flourished, and by the 1970s, the Route 128
The following highways are numbered 128:
Canada
* New Brunswick Route 128
* Ontario Highway 128 (former)
* Prince Edward Island Route 128
Costa Rica
* National Route 128
India
* National Highway 128 (India)
Japan
* Japan National Route 128 ...
corridor was dotted with high-technology
High technology (high tech), also known as advanced technology (advanced tech) or exotechnology, is technology that is at the cutting edge: the highest form of technology available. It can be defined as either the most complex or the newest te ...
companies who recruited graduates of the area's many elite institutions of higher education.
In 1987, the state received federal funding for the Central Artery/Tunnel Project. Commonly known as "the Big Dig
The Central Artery/Tunnel Project (CA/T Project), commonly known as the Big Dig, was a megaproject in Boston that rerouted the Central Artery of Interstate 93 (I-93), the chief highway through the heart of the city, into the 1.5-mile (2.4& ...
", it was, at the time, the biggest federal highway project ever approved.[Grunwald, Michael. ''Dig the Big Dig']
''The Washington Post
''The Washington Post'' (also known as the ''Post'' and, informally, ''WaPo'') is an American daily newspaper published in Washington, D.C. It is the most widely circulated newspaper within the Washington metropolitan area and has a large nati ...
''. August 6, 2006. Retrieved May 31, 2010. The project included making the Central Artery
The Central Artery (officially the John F. Fitzgerald Expressway) is a section of freeway in downtown Boston, Massachusetts; it is designated as Interstate 93, US 1 and Route 3.
The original Artery, constructed in the 1950s, was named after ...
a tunnel under downtown Boston, in addition to the re-routing of several other major highways.[ It connected areas that were once divided by elevated highway (much of the raised old Central Artery was replaced with the ]Rose Fitzgerald Kennedy Greenway
The Rose Fitzgerald Kennedy Greenway is a linear park located in several Downtown Boston neighborhoods. It consists of landscaped gardens, promenades, plazas, fountains, art, and specialty lighting systems that stretch over one mile through Chin ...
), and improved traffic conditions along with several routes.[
]
Notable 20th century politicians
 The
The Kennedy family
The Kennedy family is an American political family that has long been prominent in American politics, public service, entertainment, and business. In 1884, 35 years after the family's arrival from Ireland, Patrick Joseph "P. J." Kennedy be ...
was prominent in Massachusetts politics in the 20th century. Children of businessman and ambassador Joseph P. Kennedy Sr.
Joseph Patrick Kennedy (September 6, 1888 – November 18, 1969) was an American businessman, investor, and politician. He is known for his own political prominence as well as that of his children and was the patriarch of the Irish-American Ke ...
included John F. Kennedy
John Fitzgerald Kennedy (May 29, 1917 – November 22, 1963), often referred to by his initials JFK and the nickname Jack, was an American politician who served as the 35th president of the United States from 1961 until his assassination i ...
, who was a senator
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
and U.S. president
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States ...
before his assassination in 1963, and Ted Kennedy
Edward Moore Kennedy (February 22, 1932 – August 25, 2009) was an American lawyer and politician who served as a United States senator from Massachusetts for almost 47 years, from 1962 until his death in 2009. A member of the Democratic ...
, a senator
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
from 1962 until his death in 2009, and Eunice Kennedy Shriver
Eunice Mary Kennedy Shriver (July 10, 1921 – August 11, 2009) was an American philanthropist and a member of the Kennedy family. She was the founder of the Special Olympics, a sports organization for persons with physical and intellectual disa ...
, a co-founder of the Special Olympics
Special Olympics is the world's largest sports organization for children and adults with intellectual disabilities and physical disabilities, providing year-round training and activities to 5 million participants and Unified Sports partners in 1 ...
. In 1966, Massachusetts became the first state to directly elect an African American to the U.S. senate with Edward Brooke
Edward William Brooke III (October 26, 1919 – January 3, 2015) was an American politician of the Republican Party, who represented Massachusetts in the United States Senate from 1967 until 1979. Prior to serving in the Senate, he served as t ...
. George H. W. Bush
George Herbert Walker BushSince around 2000, he has been usually called George H. W. Bush, Bush Senior, Bush 41 or Bush the Elder to distinguish him from his eldest son, George W. Bush, who served as the 43rd president from 2001 to 2009; pr ...
, 41st President of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United Stat ...
(1989–1993) was born in Milton
Milton may refer to:
Names
* Milton (surname), a surname (and list of people with that surname)
** John Milton (1608–1674), English poet
* Milton (given name)
** Milton Friedman (1912–2006), Nobel laureate in Economics, author of '' Free t ...
in 1924. Other notable Bay State politicians on the national level included John W. McCormack
John William McCormack (December 21, 1891 – November 22, 1980) was an American politician from Boston, Massachusetts. An attorney and a Democrat, McCormack served in the United States Army during World War I, and afterwards won terms in both th ...
, Speaker of the House
The speaker of a deliberative assembly, especially a legislative body, is its presiding officer, or the chair. The title was first used in 1377 in England.
Usage
The title was first recorded in 1377 to describe the role of Thomas de Hungerf ...
in the 1960s, and Tip O'Neill
Thomas Phillip "Tip" O'Neill Jr. (December 9, 1912 – January 5, 1994) was an American politician who served as the 47th speaker of the United States House of Representatives from 1977 to 1987, representing northern Boston, Massachusetts, as ...
, whose service as Speaker of the House from 1977 to 1987 was the longest continuous tenure in United States history.
21st century
On May 17, 2004, Massachusetts became the first state in the U.S. to legalize same-sex marriage
Same-sex marriage, also known as gay marriage, is the marriage of two people of the same Legal sex and gender, sex or gender. marriage between same-sex couples is legally performed and recognized in 33 countries, with the most recent being ...
after a Massachusetts Supreme Judicial Court ruling in November 2003 determined that the exclusion of same-sex couples from the right to a civil marriage was unconstitutional.same-sex marriage in the United States
The availability of legally recognized same-sex marriage in the United States expanded from one state (Massachusetts) in 2004 to all fifty states in 2015 through various court rulings, state legislation, and direct popular votes. States each ...
in 2015.
In 2004, Massachusetts senator John Kerry
John Forbes Kerry (born December 11, 1943) is an American attorney, politician and diplomat who currently serves as the first United States special presidential envoy for climate. A member of the Forbes family and the Democratic Party (Unite ...
who won the Democratic nomination for President of the United States lost to incumbent George W. Bush
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Republican Party, Bush family, and son of the 41st president George H. W. Bush, he ...
. Eight years later, former Massachusetts governor Mitt Romney
Willard Mitt Romney (born March 12, 1947) is an American politician, businessman, and lawyer serving as the junior United States senator from Utah since January 2019, succeeding Orrin Hatch. He served as the 70th governor of Massachusetts f ...
(Republican nominee) lost to Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the U ...
in 2012. Another eight years later, Massachusetts Senator Elizabeth Warren
Elizabeth Ann Warren ( née Herring; born June 22, 1949) is an American politician and former law professor who is the senior United States senator from Massachusetts, serving since 2013. A member of the Democratic Party and regarded as a ...
was a frontrunner in the Democratic primaries for the 2020 Presidential Election, but suspended her campaign and then endorsed presumptive nominee Joe Biden.
 Two pressure cooker bombs exploded near the finish line of the
Two pressure cooker bombs exploded near the finish line of the Boston Marathon
The Boston Marathon is an annual marathon race hosted by several cities and towns in greater Boston in eastern Massachusetts, United States. It is traditionally held on Patriots' Day, the third Monday of April. Begun in 1897, the event was i ...
on April 15, 2013, at around 2:49 pm EDT. The explosions killed three people and injured an estimated 264 others. The Federal Bureau of Investigation
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the domestic intelligence and security service of the United States and its principal federal law enforcement agency. Operating under the jurisdiction of the United States Department of Justice, ...
(FBI) later identified the suspects as brothers Dzhokhar Tsarnaev
Dzhokhar "Jahar" Anzorovich Tsarnaev born July 22, 1993)russian: Джоха́р Анзо́рович Царна́ев, link=no ; ce, Царнаев Анзор-кIант ДжовхӀар o; ( Kyrgyz language, Kyrgyz: Жохар Анзор уу� ...
and Tamerlan Tsarnaev
Tamerlan Anzorovich Tsarnaev (; October 21, 1986 – April 19, 2013)russian: link=no, Тамерла́н Анзо́рович Царна́ев ; ce, Царнаев Анзор-кIант Тамерлан ; ky, Тамерлан Анзор уул ...
. The ensuing manhunt
Manhunt may refer to:
Search processes
* Manhunt (law enforcement), a search for a dangerous fugitive
* Manhunt (military), a search for a high-value target by special operations forces or intelligence agencies
Social organisations
* Manhun ...
ended on April 19 when thousands of law enforcement officers searched a 20-block area of nearby Watertown Watertown may refer to:
Places in China
In China, a water town is a type of ancient scenic town known for its waterways.
Places in the United States
*Watertown, Connecticut, a New England town
**Watertown (CDP), Connecticut, the central village ...
. Dzhokhar later said he was motivated by extremist Islamic
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the mai ...
beliefs and learned to build explosive devices from ''Inspire'', the online magazine of al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula
Al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula ( ar-at, تنظيم القاعدة في جزيرة العرب, Tanẓīm al-Qā‘idah fī Jazīrat al-‘Arab, lit=Organization of the Base in the Arabian Peninsula or , ''Tanẓīm Qā‘idat al-Jihād fī Jaz ...
.
On November 8, 2016, Massachusetts voted in favor of the Massachusetts Marijuana Legalization Initiative, also known as Question 4. It was included in the 2016 United States presidential election
The 2016 United States presidential election was the 58th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 8, 2016. The Republican ticket of businessman Donald Trump and Indiana governor Mike Pence defeated the Democratic ticket ...
ballot in Massachusetts as an indirectly initiated state statute.
Geography
 Massachusetts is the 7th-smallest state in the United States. It is located in the
Massachusetts is the 7th-smallest state in the United States. It is located in the New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
region of the Northeastern United States
The Northeastern United States, also referred to as the Northeast, the East Coast, or the American Northeast, is a geographic region of the United States. It is located on the Atlantic coast of North America, with Canada to its north, the Southe ...
and has an area of , 25.7% of which is water. Several large bays distinctly shape its coast. Boston is the largest city, at the inmost point of Massachusetts Bay
Massachusetts Bay is a bay on the Gulf of Maine that forms part of the central coastline of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts.
Description
The bay extends from Cape Ann on the north to Plymouth Harbor on the south, a distance of about . Its ...
, and the mouth of the Charles River
The Charles River ( Massachusett: ''Quinobequin)'' (sometimes called the River Charles or simply the Charles) is an river in eastern Massachusetts. It flows northeast from Hopkinton to Boston along a highly meandering route, that doubles b ...
.
Despite its small size, Massachusetts features numerous topography, topographically distinctive regions. The large coastal plain of the Atlantic Ocean in the eastern section of the state contains Greater Boston
Greater Boston is the metropolitan region of New England encompassing the municipality of Boston (the capital of the U.S. state of Massachusetts and the most populous city in New England) and its surrounding areas. The region forms the northern ar ...
, along with most of the state's population,Connecticut River Valley
The Connecticut River is the longest river in the New England region of the United States, flowing roughly southward for through four states. It rises 300 yards (270 m) south of the U.S. border with Quebec, Canada, and discharges at Long Island ...
. Along the western border of Western Massachusetts lies the highest elevated part of the state, the Berkshires, forming a portion of the northern terminus of the Appalachian Mountains.
The U.S. National Park Service administers a number of natural and historical List of areas in the National Park System in Massachusetts, sites in Massachusetts.[ In addition, the Department of Conservation and Recreation maintains a number of List of Massachusetts state parks, parks, trails, and beaches throughout Massachusetts.
]
Ecology
The primary biome of inland Massachusetts is temperate deciduous forest.
Although much of Massachusetts had been cleared for agriculture, leaving only traces of old-growth forest in isolated pockets, secondary growth has regenerated in many rural areas as farms have been abandoned. Currently, forests cover around 62% of Massachusetts. The areas most affected by human development include the Greater Boston area in the east and the Springfield metropolitan area in the west, although the latter includes agricultural areas throughout the Connecticut River Valley. There are currently 219 endangered species in Massachusetts.
A number of species are doing well in the increasingly urbanized Massachusetts. Peregrine falcons utilize office towers in larger cities as nesting areas, and the population of coyotes, whose diet may include garbage and roadkill, has been increasing in recent decades. White-tailed deer, raccoons, wild turkeys, and eastern gray squirrels are also found throughout Massachusetts. In more rural areas in the western part of Massachusetts, larger mammals such as moose and American black bear, black bears have returned, largely due to reforestation following the regional decline in agriculture.
Massachusetts is located along the Atlantic Flyway, a major route for migratory waterfowl along the eastern coast. Lakes in central Massachusetts provide habitat for many species of fish and waterfowl, but some species such as the common loon are becoming rare. A significant population of long-tailed ducks winter off Nantucket
Nantucket () is an island about south from Cape Cod. Together with the small islands of Tuckernuck and Muskeget, it constitutes the Town and County of Nantucket, a combined county/town government that is part of the U.S. state of Massachuse ...
. Small offshore islands and beaches are home to roseate terns and are important breeding areas for the locally threatened piping plover. Protected areas such as the Monomoy National Wildlife Refuge provide critical breeding habitat for shorebirds and a variety of marine wildlife including a large population of grey seals. Since 2009, there has been a significant increase in the number of Great white sharks spotted and tagged in the coastal waters off of Cape Cod.
Freshwater fish species in Massachusetts include Bass (fish), bass, Common carp, carp, catfish, and trout, while saltwater species such as Atlantic cod, haddock, and American lobster populate offshore waters. Other marine species include Harbor seals, the endangered North Atlantic right whales, as well as humpback whales, fin whales, minke whales, and Atlantic white-sided dolphins.
The European corn borer, a significant agricultural pest, was first found in North America near Boston, Massachusetts in 1917.
Climate
Most of Massachusetts has a humid continental climate, with cold winters and warm summers. Far southeast coastal areas are the broad transition zone to Humid Subtropical climates. The warm to hot summers render the oceanic climate rare in this transition, only applying to exposed coastal areas such as on the peninsula of Barnstable County, Massachusetts, Barnstable County. The climate of Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
is quite representative for the commonwealth, characterized by summer highs of around and winter highs of , and is quite wet. Frosts are frequent all winter, even in coastal areas due to prevailing inland winds. Due to its location near the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Massachusetts is vulnerable to nor'easters, tropical cyclone, hurricanes and tropical storms.

Environmental issues
Climate change
Climate change in Massachusetts will affect both urban and rural environments, including forestry, fisheries, agriculture, and coastal development.Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
alone, costs of climate change-related storms will result in 5 to 100 billion dollars in damage.
Power Initiatives
The State of Massachusetts has developed a plethora of incentives to encourage the implementation of renewable energy and efficient appliances and home facilities. The Mass Save program has been formed in conjunction with the State by several companies that provide power & gas in Massachusetts in order to provide homeowners and renters with incentives to retrofit their homes with efficient HVAC equipment and other household appliances. Appliances such as water heaters, air conditioners, washers and driers, and heat pumps are eligible for rebates in order to incentivize change.
The concept of Mass Save was created in 2008 by the passing of the Green Communities Act of 2008 during Deval Patrick's tenure as governor. The main goal of the Green Communities Act was to reduce the consumption of fossil fuels in the State and to encourage new, more efficient technologies. Among others, one result of this act was a requirement for Program Administrators of utilities to invest in saving energy, as opposed to purchasing and generating additional energy where economically feasible. In Massachusetts, eleven Program Administrators, including Eversource, National Grid, Western Massachusetts Electric, Cape Light Compact, Until, and Berkshire Gas, jointly own the rights to this program, in conjunction with the MA Department of Energy Resources (DOER) and the Energy Efficiency Advisory Council (EEAC).
Mass Save also conducts no-cost in-home energy assessments so that homeowners, renters, and small business owners may educate themselves about energy efficiency-related home improvements and find opportunities to save money and energy. During the home assessment, Mass Save provides ENERGY STAR certified LED light bulbs, power strips, low flow showerheads, faucet aerators, and efficient thermostats free of charge. Additionally, air leaks will be detected in the home or building and patched, and recommendations will be made to install additional Thermal insulation, insulation to decrease the loss of heated or cooled air. Discounts of 75 percent or more are available on these insulation improvements. Due to COVID-19, Mass Save is currently conducting assessments remotely. Residents can schedule a remote assessment using the program's website or phone line.
The State Revenue Service provides incentives for the installation of solar panels. In addition to the Federal Residential Renewable energy credit, Massachusetts residents may be eligible for a tax credit of up to 15 percent of the project. Once installed, arrays are eligible for net metering. Certain municipalities will offer up to $1.20 per watt, up to 50 percent of the system's cost on PV arrays 25 kW or less. The Massachusetts Department of Energy Resources also offers low-interest, fixed-rate financing with loan support for low-income residents. This program is currently set to terminate on December 31, 2020.
As a part of the Massachusetts Department of Energy Resources' effort to incentivize the usage of renewable energy, the MOR-EV, or Massachusetts Offers Rebates for Electric Vehicles initiative was created. With this incentive, residents may qualify for a State incentive of up to $2,500 dollars for the purchase or lease of an electric vehicle, or $1,500 for the purchase or lease of a plug-in hybrid vehicle. This rebate is available in addition to the tax credits offered by the United States Department of Energy for the purchase of electric and plug-in hybrid vehicles.
For income-eligible residents, Mass Save has partnered with Massachusetts Community Action Program Agencies and Low-Income Energy Affordability Network (LEAN) to offer residents assistance with upgrades to their homes that will result in more efficient energy usage. Residents may qualify for a replacement of their heating system, insulation installation, appliances, and thermostats if they meet the income qualifications provided on Mass Save's website. For residents of 5+ family residential buildings, there are additional income-restricted benefits available through LEAN. If at least 50 percent of the residents of the building qualify as low income, energy efficiency improvements like those available through Mass Save are available. Residential structures operated by non-profit organizations, for profit operations, or housing authorities may take advantage of these programs.
In late 2020, the Baker Administration released a Decarbonization Roadmap that aims for net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050. The plan calls for major investments in offshore wind and solar energy and would require all new automobiles sold to be zero-emissions (electric or hydrogen powered) by 2035.
Demographics
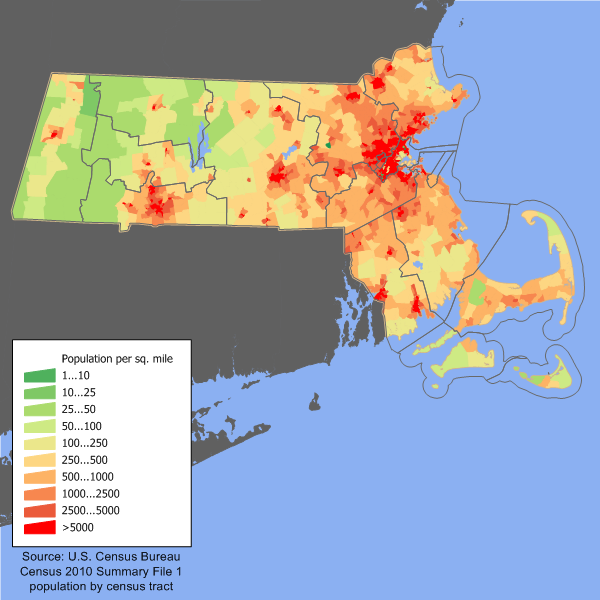 At the 2020 United States census, 2020 U.S. census, Massachusetts had a population of over 7 million, a 7.4% increase since the 2010 United States Census, 2010 United States census.
At the 2020 United States census, 2020 U.S. census, Massachusetts had a population of over 7 million, a 7.4% increase since the 2010 United States Census, 2010 United States census.Rhode Island
Rhode Island (, like ''road'') is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is the List of U.S. states by area, smallest U.S. state by area and the List of states and territories of the United States ...
. In 2014, Massachusetts had 1,011,811 foreign-born residents or 15% of the population.[ As of July 2021, the population is estimated to have fallen to 6.98 million.
Most Bay State residents live within the Boston metropolitan area, also known as ]Greater Boston
Greater Boston is the metropolitan region of New England encompassing the municipality of Boston (the capital of the U.S. state of Massachusetts and the most populous city in New England) and its surrounding areas. The region forms the northern ar ...
, which includes Boston and its proximate surroundings but also extending to Greater Lowell and to Worcester, Massachusetts, Worcester. The Springfield metropolitan area, Massachusetts, Springfield metropolitan area, also known as Greater Springfield, is also a major center of population. Demographically, the center of population of Massachusetts is located in the town of Natick, Massachusetts, Natick.
Like the rest of the Northeastern United States
The Northeastern United States, also referred to as the Northeast, the East Coast, or the American Northeast, is a geographic region of the United States. It is located on the Atlantic coast of North America, with Canada to its north, the Southe ...
, the population of Massachusetts has continued to grow in the late 20th and early 21st centuries. Massachusetts is the fastest-growing state in New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
and the 25th fastest-growing state in the United States.[
Foreign immigration is also a factor in the state's population growth, causing the state's population to continue to grow as of the 2010 United States Census, 2010 census (particularly in Massachusetts gateway cities where costs of living are lower).][ Many areas of Massachusetts showed relatively stable population trends between 2000 and 2010.][ Exburb, Exurban Boston and coastal areas grew the most rapidly, while Berkshire County, Massachusetts, Berkshire County in far Western Massachusetts and Barnstable County on Cape Cod were the only counties to lose population as of the 2010 United States Census, 2010 census.][
By sex, 48.4% were male, and 51.6% were female in 2014. In terms of age, 79.2% were over 18 and 14.8% were over 65.][
]
Race and ancestry
 The state's most populous ethnic group, non-Hispanic white, has declined from 95.4% in 1970 to 67.6% in 2020.
The state's most populous ethnic group, non-Hispanic white, has declined from 95.4% in 1970 to 67.6% in 2020.[ As of 2011, non-Hispanic whites were involved in 63.6% of all the births, while 36.4% of the population of Massachusetts younger than age1 was minorities (at least one parent who was not non-Hispanic white). One major reason for this is that non-Hispanic whites in Massachusetts recorded a total fertility rate of 1.36 in 2017, the second-lowest in the country after neighboring Rhode Island.
As late as 1795, the population of Massachusetts was nearly 95% of English ancestry. During the early and mid-19th century, immigrant groups began arriving in Massachusetts in large numbers; first from Ireland in the 1840s; today the Irish and part-Irish are the largest ancestry group in the state at nearly 25% of the total population. Others arrived later from Quebec as well as places in Europe such as Italy, Portugal, and Poland. In the early 20th century, a number of Great Migration (African American), African Americans migrated to Massachusetts, although in somewhat fewer numbers than many other Northern states. Later in the 20th century, immigration from Latin America increased considerably. More than 156,000 Chinese Americans in Boston, Chinese Americans made their home in Massachusetts in 2014, and Boston hosts a growing Chinatown, Boston, Chinatown accommodating heavily traveled Chinatown bus lines, Chinese-owned bus lines to and from Chinatown, Manhattan in New York City. Massachusetts also has large Dominican American, Dominican, Puerto Rican American, Puerto Rican, Haitian Americans, Haitian, Cape Verdean American, Cape Verdean and Brazilian American, Brazilian populations. Boston's South End, Boston, South End and Jamaica Plain are both gay villages, as is nearby Provincetown, Massachusetts on Cape Cod.
] The largest ancestry group in Massachusetts are the Irish Americans, Irish (22.5% of the population), who live in significant numbers throughout the state but form more than 40% of the population along the South Shore in Norfolk and Plymouth counties (in both counties overall, Irish-Americans comprise more than 30% of the population). Italian Americans, Italians form the second-largest ethnic group in the state (13.5%), but form a plurality in some suburbs north of Boston and in a few towns in the Berkshires. English Americans, the third-largest (11.4%) group, form a plurality in some western towns. French Americans, French and French Canadians also form a significant part (10.7%), with sizable populations in Bristol, Hampden, and Worcester Counties, along with Middlesex county especially concentrated in the areas surrounding Lowell and Lawrence.
The largest ancestry group in Massachusetts are the Irish Americans, Irish (22.5% of the population), who live in significant numbers throughout the state but form more than 40% of the population along the South Shore in Norfolk and Plymouth counties (in both counties overall, Irish-Americans comprise more than 30% of the population). Italian Americans, Italians form the second-largest ethnic group in the state (13.5%), but form a plurality in some suburbs north of Boston and in a few towns in the Berkshires. English Americans, the third-largest (11.4%) group, form a plurality in some western towns. French Americans, French and French Canadians also form a significant part (10.7%), with sizable populations in Bristol, Hampden, and Worcester Counties, along with Middlesex county especially concentrated in the areas surrounding Lowell and Lawrence.Wampanoag
The Wampanoag , also rendered Wôpanâak, are an Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands based in southeastern Massachusetts and historically parts of eastern Rhode Island,Salwen, "Indians of Southern New England and Long Island," p. 17 ...
tribe maintains reservations at Aquinnah, Massachusetts, Aquinnah on Martha's Vineyard and at Mashpee, Massachusetts, Mashpee on Cape Cod—with an ongoing Massachusett language, native language revival project underway since 1993, while the Nipmuc
The Nipmuc or Nipmuck people are an Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands, who historically spoke an Eastern Algonquian language. Their historic territory Nippenet, "the freshwater pond place," is in central Massachusetts and nearby part ...
maintain two state-recognized reservations in the central part of the state, including one at Grafton, Massachusetts, Grafton.
Massachusetts has avoided many forms of racial strife seen elsewhere in the US, but examples such as the successful electoral showings of the Nativism (politics), nativist (mainly Anti-Catholicism, anti-Catholic) Know Nothings in the 1850s, the controversial Sacco and Vanzetti executions in the 1920s, and Boston's opposition to Boston busing desegregation, desegregation busing in the 1970s show that the ethnic history of Massachusetts was not completely harmonious.
Languages
The most common varieties of American English spoken in Massachusetts, other than General American, are the New England English#Southwestern New England, ''cot-caught'' distinct, rhotic, western Massachusetts dialect and the Boston accent, ''cot-caught'' merged, non-rhotic, eastern Massachusetts dialect (popularly known as a "Boston accent").
As of 2010, 78.93% (4,823,127) of Massachusetts residents5 and older spoke English at home as a first language, while 7.50% (458,256) spoke Spanish, 2.97% (181,437) Portuguese language, Portuguese, 1.59% (96,690) Chinese (which includes Cantonese and Standard Chinese, Mandarin), 1.11% (67,788) French, 0.89% (54,456) French-based creole languages, French Creole, 0.72% (43,798) Italian, 0.62% (37,865) Russian, and Vietnamese language, Vietnamese was spoken as a primary language by 0.58% (35,283) of the population over5. In total, 21.07% (1,287,419) of Massachusetts's population5 and older spoke a first language other than English.
Religion
 Massachusetts was founded and settled by Brownist
Massachusetts was founded and settled by Brownist Puritans
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to purify the Church of England of Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should become more Protestant. P ...
in 1620[ and soon after by other groups of Ecclesiastical separatism, Separatists/English Dissenters, Dissenters, Nonconformist (Protestantism), Nonconformists and Independent (religion), Independents from 17th-century denominations in England, 17th century England. A majority of people in Massachusetts today remain Christians.][ The descendants of the Puritans belong to many different churches; in the direct line of inheritance are the various Congregational churches, the United Church of Christ and congregations of the Unitarian Universalist Association. The headquarters of the Unitarian Universalist Association, long located on Beacon Hill, Boston, Beacon Hill, is now located in South Boston. Many Puritan descendants also dispersed to other Protestant denominations. Some disaffiliated along with Roman Catholics and other Christian groups in the wake of modern secularization.
As of the 2014 Pew study, Christians made up 57% of the state's population, with Protestantism, Protestants making up 21% of them. Catholic Church, Roman Catholics made up 34% and now predominate because of massive immigration from primarily Catholic countries and regions—chiefly Ireland, Italy, Poland, Portugal, Quebec, and Latin America. Both Protestant and Roman Catholic communities have been in decline since the late 20th century, due to the rise of irreligion in ]New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
. It is the most irreligious region of the country, along with the Western United States; for comparison and contrast however, in 2020, the Public Religion Research Institute determined 67% of the population were Christian reflecting a slight increase of religiosity.
Education
 In 2018, Massachusetts's overall educational system was ranked the top among all fifty U.S. states by ''U.S. News & World Report''. Massachusetts was the first state in North America to require municipalities to appoint a teacher or establish a grammar school with the passage of the Massachusetts School Laws, Massachusetts Education Law of 1647, and 19th century reforms pushed by
In 2018, Massachusetts's overall educational system was ranked the top among all fifty U.S. states by ''U.S. News & World Report''. Massachusetts was the first state in North America to require municipalities to appoint a teacher or establish a grammar school with the passage of the Massachusetts School Laws, Massachusetts Education Law of 1647, and 19th century reforms pushed by Horace Mann
Horace Mann (May 4, 1796August 2, 1859) was an American educational reformer, slavery abolitionist and Whig politician known for his commitment to promoting public education. In 1848, after public service as Secretary of the Massachusetts Sta ...
laid much of the groundwork for contemporary universal public education which was established in 1852.Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher le ...
, founded in 1636), and its oldest women's college (Mount Holyoke College, founded in 1837). Massachusetts is also home to the highest ranked private high school in the United States, Phillips Academy in Andover, Massachusetts, which was founded in 1778.
Massachusetts's per-student public expenditure for elementary and secondary schools was eighth in the nation in 2012, at $14,844. In 2013, Massachusetts scored highest of all the states in math and third-highest in reading on the National Assessment of Educational Progress. Massachusetts' public-school students place among the top tier in the world in academic performance.Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher le ...
and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, both located in Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge bec ...
, consistently rank among the world's best private universities and universities in general. In addition to Harvard and MIT, several other Massachusetts universities currently rank in the top 50 at the undergraduate level nationally in the College and university rankings#United States, widely cited rankings of ''U.S. News & World Report'': Tufts University (#27), Boston College (#32), Brandeis University (#34), Boston University (#37) and Northeastern University (#40). Massachusetts is also home to three of the top five ''U.S. News & World Report''s best Liberal Arts Colleges: Williams College (#1), Amherst College (#2), and Wellesley College (#4). Boston Architectural College is New England's largest private college of spatial design. The public University of Massachusetts (nicknamed ''UMass'') features five campuses in the state, with its University of Massachusetts Amherst, flagship campus in Amherst, Massachusetts, Amherst, which enrolls more than 25,000.
Economy
The United States Bureau of Economic Analysis estimates that the Massachusetts gross state product in 2020 was $584billion. The Per capita personal income in the United States, per capita personal income in 2012 was $53,221, making it the third-highest state in the nation. As of January 2022, Massachusetts state general minimum wage is $14.25 per hour while the minimum wage for tipped workers is $6.15 an hour, with a guarantee that employers will pay the difference should a tipped employee's hourly wage not meet or exceed the general minimum wage. This wage is set to increase to a general minimum of $15.00 per hour and a tipped worker minimum of $6.75 per hour in January 2023, as part of a series of minimum wage amendments passed in 2018 that saw the minimum wage increase slowly every January up to 2023.
In 2015, twelve Fortune 500, ''Fortune'' 500 companies were located in Massachusetts: Liberty Mutual, Massachusetts Mutual Life Insurance Company, TJX Companies, General Electric, Raytheon, American Tower, Global Partners, Thermo Fisher Scientific, State Street Corporation, Biogen, Eversource Energy, and Boston Scientific. CNBC's list of "Top States for Business for 2014" has recognized Massachusetts as the 25th-best state in the nation for business, and for the second year in a row the state was ranked by Bloomberg as the most innovative state in America. According to a 2013 study by Phoenix Marketing International, Massachusetts had the sixth-largest number of millionaires per capita in the United States, with a ratio of 6.73 percent. Billionaires living in the state include past and present leaders (and related family) of local companies such as Fidelity Investments, New Balance, Kraft Group, Boston Scientific, and the former Continental Cablevision.
Massachusetts has three Foreign-trade zones of the United States, foreign-trade zones, the Massachusetts Port Authority of Boston, the Port of New Bedford, and the City of Holyoke. Logan International Airport, Boston-Logan International Airport is the busiest airport in New England, serving 33.4million total passengers in 2015, and witnessing rapid growth in international air traffic since 2010.[ Accessed May 8, 2016.]
Sectors vital to the Massachusetts economy include higher education, biotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used b ...
, information technology, finance, health care, tourism, manufacturing, and defense. The Route 128 (Massachusetts), Route 128 corridor and Greater Boston continue to be a major center for venture capital, venture capital investment, and high technology remains an important sector. In recent years tourism has played an ever-important role in the state's economy, with Boston and Cape Cod being the leading destinations. Other popular tourist destinations include Salem
Salem may refer to: Places
Canada
Ontario
* Bruce County
** Salem, Arran–Elderslie, Ontario, in the municipality of Arran–Elderslie
** Salem, South Bruce, Ontario, in the municipality of South Bruce
* Salem, Dufferin County, Ontario, part ...
, Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west.
Plymouth ...
, and the Berkshires. Massachusetts is the sixth-most popular tourist destination for foreign travelers. In 2010, the Great Places in Massachusetts Commission published '1,000 Great Places in Massachusetts' that identified 1,000 sites across the commonwealth to highlight the diverse historic, cultural, and natural attractions.
 While manufacturing comprised less than 10% of Massachusetts's gross state product in 2016, the Commonwealth ranked 16th in the nation in total manufacturing output in the United States. This includes a diverse array of manufactured goods such as medical devices, paper goods, specialty chemicals and plastics, telecommunications and electronics equipment, and machined components.
The more than 33,000 nonprofits in Massachusetts employ one-sixth of the state's workforce. In 2007, Governor Deval Patrick signed into law a state holiday, Nonprofit Awareness Day.
In February 2017, ''U.S. News & World Report'' ranked Massachusetts the best state in the United States based upon 60 Performance metric, metrics including healthcare, education, crime, infrastructure, opportunity, economy, and government. The Bay State ranked number one in education, number two in healthcare, and number five in the handling of the economy.
While manufacturing comprised less than 10% of Massachusetts's gross state product in 2016, the Commonwealth ranked 16th in the nation in total manufacturing output in the United States. This includes a diverse array of manufactured goods such as medical devices, paper goods, specialty chemicals and plastics, telecommunications and electronics equipment, and machined components.
The more than 33,000 nonprofits in Massachusetts employ one-sixth of the state's workforce. In 2007, Governor Deval Patrick signed into law a state holiday, Nonprofit Awareness Day.
In February 2017, ''U.S. News & World Report'' ranked Massachusetts the best state in the United States based upon 60 Performance metric, metrics including healthcare, education, crime, infrastructure, opportunity, economy, and government. The Bay State ranked number one in education, number two in healthcare, and number five in the handling of the economy.
Agriculture
As of 2012, there were 7,755 farms in Massachusetts encompassing a total of , averaging apiece. Greenhouse, floriculture, and sod products including ornamental plant, the ornamental market make up more than one third of the state's agricultural output.
Taxation
Depending on how it is calculated, state and local tax burden in Massachusetts has been estimated among U.S. states and Washington D.C. as 21st-highest (11.44% or $6,163 per year for a household with nationwide median income) or 25th-highest overall with below-average corporate taxes (39th-highest), above-average personal income taxes, (13th-highest), above-average sales tax (18th-highest), and below-average property taxes (46th-highest). In the 1970s, the Commonwealth ranked as a relatively high-tax state, gaining the pejorative nickname "Taxachusetts". This was followed by a round of tax limitations during the 1980s—a conservative period in American politics—including Proposition 2½.
As of January 1, 2020, Massachusetts has a flat-rate personal income tax of 5.00%, after a 2002 voter referendum to eventually lower the rate to 5.0% as amended by the legislature. There is a tax exemption for income below a threshold that varies from year to year. The corporate income tax rate is 8.8%,[ on retail sales of tangible personal property—except for groceries, clothing (up to $175.00), and periodicals.][ Massachusetts also charges a use tax when goods are bought from other states and the vendor does not remit Massachusetts sales tax; taxpayers report and pay this on their income tax forms or dedicated forms, though there are "safe harbor" amounts that can be paid without tallying up actual purchases (except for purchases over $1,000).][
]
Energy
Massachusetts's electricity generation market was made competitive in 1998, enabling retail customers to change suppliers without changing utility companies. In 2018, Massachusetts consumed 1,459trillion British Thermal Units, BTU,[ In 2014 and 2015, Massachusetts was ranked as the most energy efficient state the United States while Boston is the most efficient city, but it had the fourth-highest average residential retail electricity prices of any state.][ In 2018, renewable energy was about 7.2 percent of total energy consumed in the state, ranking 34th.][
]
Transportation
 Massachusetts has 10 regional metropolitan planning organizations and three non-metropolitan planning organizations covering the remainder of the state; statewide planning is handled by the Massachusetts Department of Transportation. Transportation is the single largest source of greenhouse gas emissions by economic sector in Massachusetts.
Massachusetts has 10 regional metropolitan planning organizations and three non-metropolitan planning organizations covering the remainder of the state; statewide planning is handled by the Massachusetts Department of Transportation. Transportation is the single largest source of greenhouse gas emissions by economic sector in Massachusetts.
Regional public transportation
The Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA), also known as "TheT", operates public transportation in the form of subway, bus, and ferry systems in the Greater Boston, Metro Boston area.
Fifteen other regional transit authorities provide public transportation in the form of bus services in the rest of the state. Four heritage railways are also in operation:
* The Cape Cod Central Railroad, operating from Hyannis to Buzzard's Bay
* The Berkshire Scenic Railway Museum, Berkshire Scenic Railway, operating from Lee to Great Barrington
* Edaville Railroad in Carver
* The National Streetcar Museum, Lowell National Historical Park Trolley Line in Lowell
Long-distance rail and bus
Amtrak operates several inter-city rail lines connecting Massachusetts. Boston's South Station serves as the terminus for three lines, namely the high-speed ''Acela Express'', which links to cities such as Providence, Rhode Island, Providence, New Haven, Connecticut, New Haven, New York City, and eventually Washington DC; the ''Northeast Regional'', which follows the same route but includes many more stops, and also continues further south to Newport News, Virginia, Newport News in Virginia; and the ''Lake Shore Limited'', which runs westward to Worcester, Massachusetts, Worcester, Springfield
Springfield may refer to:
* Springfield (toponym), the place name in general
Places and locations Australia
* Springfield, New South Wales (Central Coast)
* Springfield, New South Wales (Snowy Monaro Regional Council)
* Springfield, Queenslan ...
, and eventually Chicago, Illinois, Chicago.Springfield
Springfield may refer to:
* Springfield (toponym), the place name in general
Places and locations Australia
* Springfield, New South Wales (Central Coast)
* Springfield, New South Wales (Snowy Monaro Regional Council)
* Springfield, Queenslan ...
to New Haven, Connecticut, New Haven, operated in conjunction with the Connecticut Department of Transportation, and the ''Valley Flyer (Amtrak train), Valley Flyer'' runs a similar route but continues further north to Greenfield, Massachusetts, Greenfield. Several stations in western Massachusetts are also served by the ''Vermonter (train), Vermonter'', which connects St. Albans station (Vermont), St. Albans, Vermont to Washington DC.Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west.
Plymouth ...
. This overlaps with the service areas of neighboring regional transportation authorities. As of the summer of 2013 the Cape Cod Regional Transit Authority in collaboration with the MBTA and the Massachusetts Department of Transportation (MassDOT) is operating the CapeFLYER providing passenger rail service between Boston and Cape Cod.
Ferry
Ferry services are operated throughout different regions of the states.
Most ports north of Cape Cod are served by Boston Harbor Cruises, which operates MBTA Boat, ferry services in and around Greater Boston
Greater Boston is the metropolitan region of New England encompassing the municipality of Boston (the capital of the U.S. state of Massachusetts and the most populous city in New England) and its surrounding areas. The region forms the northern ar ...
under contract with the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority. Several routes connect the downtown area with Hingham, Massachusetts, Hingham, Hull, Massachusetts, Hull, Winthrop, Massachusetts, Winthrop, Salem
Salem may refer to: Places
Canada
Ontario
* Bruce County
** Salem, Arran–Elderslie, Ontario, in the municipality of Arran–Elderslie
** Salem, South Bruce, Ontario, in the municipality of South Bruce
* Salem, Dufferin County, Ontario, part ...
, Logan Airport, Charlestown, Massachusetts, Charlestown, and some of the islands located within the harbor. The same company also operates seasonal service between Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
and Provincetown.
On the southern shore of the state, several different passenger ferry lines connect Martha's Vineyard
Martha's Vineyard, often simply called the Vineyard, is an island in the Northeastern United States, located south of Cape Cod in Dukes County, Massachusetts, known for being a popular, affluent summer colony. Martha's Vineyard includes the s ...
to ports along the mainland, including Woods Hole, Massachusetts, Woods Hole, Hyannis, Massachusetts, Hyannis, New Bedford, Massachusetts, New Bedford, and Falmouth, Massachusetts, Falmouth, all in Massachusetts, as well as North Kingstown, Rhode Island, North Kingstown in Rhode Island, Highlands, New Jersey, Highlands in New Jersey, and New York City in New York. Similarly, several different lines connect Nantucket
Nantucket () is an island about south from Cape Cod. Together with the small islands of Tuckernuck and Muskeget, it constitutes the Town and County of Nantucket, a combined county/town government that is part of the U.S. state of Massachuse ...
to ports including Hyannis, New Bedford, Harwich, Massachusetts, Harwich, and New York City. Service between the two islands is also offered. The dominant companies serving these routes include SeaStreak, Hy-Line Cruises, and The Steamship Authority, the latter of which regulates all passenger services in the region and is also the only company permitted to offer freight ferry services to the islands.
Other ferry connections in the state include a line between Fall River, Massachusetts, Fall River and Block Island via Newport, Rhode Island, Newport, seasonal ferry service connecting Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west.
Plymouth ...
to Provincetown, and a service between New Bedford and Cuttyhunk.
Rail freight
As of 2018, a number of Rail freight transport, freight railroads were operating in Massachusetts, with Class I railroad CSX Transportation, CSX being the largest carrier, and another Class 1, Norfolk Southern serving the state via its Pan Am Southern joint partnership. Several regional and short line railroads also provide service and connect with other railroads. Massachusetts has a total of of freight trackage in operation.
Air service
 Logan International Airport, Boston Logan International Airport served 33.5million passengers in 2015 (up from 31.6million in 2014)
Logan International Airport, Boston Logan International Airport served 33.5million passengers in 2015 (up from 31.6million in 2014)[ through 103 Gate (airport), gates.][ Massachusetts has 39 public-use airfields and more than 200 private landing spots. Some airports receive funding from the Aeronautics Division of the Massachusetts Department of Transportation and the Federal Aviation Administration; the FAA is also the primary regulator of Massachusetts air travel.
]
Roads
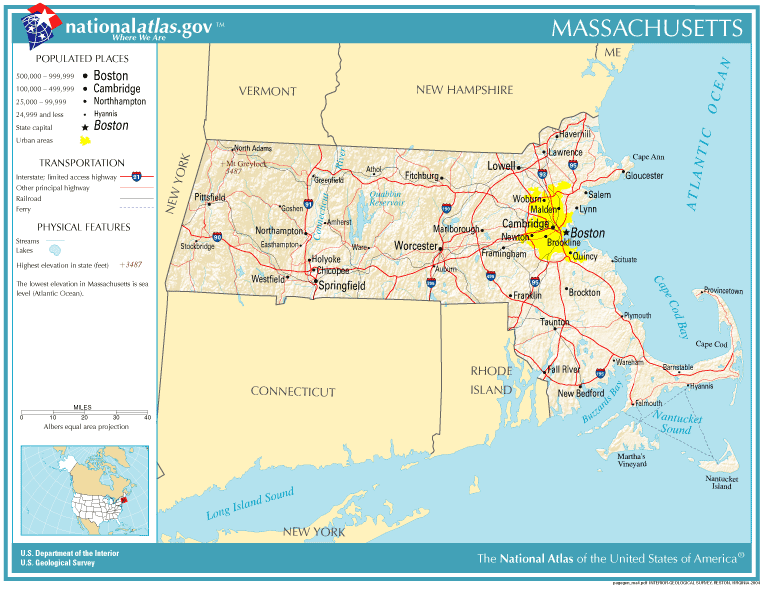 There are a total of of Interstate highway, interstates and other highways in Massachusetts. Massachusetts Turnpike, Interstate90 (I-90, also known as the Massachusetts Turnpike), is the longest interstate in Massachusetts. The route travels generally west to east, entering Massachusetts at the New York state line in the town of West Stockbridge, Massachusetts, West Stockbridge, and passes just north of
There are a total of of Interstate highway, interstates and other highways in Massachusetts. Massachusetts Turnpike, Interstate90 (I-90, also known as the Massachusetts Turnpike), is the longest interstate in Massachusetts. The route travels generally west to east, entering Massachusetts at the New York state line in the town of West Stockbridge, Massachusetts, West Stockbridge, and passes just north of Springfield
Springfield may refer to:
* Springfield (toponym), the place name in general
Places and locations Australia
* Springfield, New South Wales (Central Coast)
* Springfield, New South Wales (Snowy Monaro Regional Council)
* Springfield, Queenslan ...
, just south of Worcester, Massachusetts, Worcester and through Framingham, Massachusetts, Framingham before terminating near Logan International Airport in Boston. Other major interstates include Interstate 91 in Massachusetts, I-91, which travels generally north and south along the Connecticut River; Interstate 93 in Massachusetts, I-93, which travels north and south through central Boston, then passes through Methuen, Massachusetts, Methuen before entering New Hampshire; and Interstate 95 in Massachusetts, I-95, which connects Providence, Rhode Island with Greater Boston, forming a partial beltway, loop Concurrency (road), concurrent with Massachusetts Route 128, Route128 around the more urbanized areas before continuing north along the coast into New Hampshire.
Interstate 495 (Massachusetts), I-495 forms a wide loop around the outer edge of Greater Boston. Other major interstates in Massachusetts include Interstate 291 (Massachusetts), I-291, Interstate 391 (Massachusetts), I-391, Interstate 84 in Massachusetts, I-84, Interstate 195 in Massachusetts, I-195, Interstate 395 in Massachusetts, I-395, Interstate 290 (Massachusetts), I-290, and Interstate 190 (Massachusetts), I-190. Major non-interstate highways in Massachusetts include United States Numbered Highways, U.S. Routes U.S. Route 1 in Massachusetts, 1, U.S. Route 3 in Massachusetts, 3, U.S. Route 6 in Massachusetts, 6, and U.S. Route 20 in Massachusetts, 20, and state routes Massachusetts Route 2, 2, Massachusetts Route 3, 3, 9, Massachusetts Route 24, 24, and 128. A great majority of interstates in Massachusetts were constructed during the mid-20th century, and at times were controversial, particularly the intent Southwest Corridor (Massachusetts), to route I-95 northeastwards from Providence, Rhode Island, directly through central Boston, first proposed in 1948. Opposition to continued construction grew, and in 1970 Governor Francis W. Sargent issued a general prohibition on most further freeway construction within the I-95/Route 128 loop in the Boston area. A massive undertaking to bring I-93 underground in downtown Boston, called the Big Dig
The Central Artery/Tunnel Project (CA/T Project), commonly known as the Big Dig, was a megaproject in Boston that rerouted the Central Artery of Interstate 93 (I-93), the chief highway through the heart of the city, into the 1.5-mile (2.4& ...
, brought the city's highway system under public scrutiny for its high cost and construction quality.[
]
Government and politics
 Massachusetts has a long political history; earlier political structures included the Mayflower Compact of 1620, the separate Massachusetts Bay Colony, Massachusetts Bay and Plymouth Colony, Plymouth colonies, and the combined colonial Province of Massachusetts. The
Massachusetts has a long political history; earlier political structures included the Mayflower Compact of 1620, the separate Massachusetts Bay Colony, Massachusetts Bay and Plymouth Colony, Plymouth colonies, and the combined colonial Province of Massachusetts. The Massachusetts Constitution
The Constitution of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts is the fundamental governing document of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, one of the 50 individual state governments that make up the United States of America. As a member of the Massachuset ...
was ratified in 1780 while the American Revolutionary War, Revolutionary War was in progress, four years after the Articles of Confederation
The Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union was an agreement among the 13 Colonies of the United States of America that served as its first frame of government. It was approved after much debate (between July 1776 and November 1777) by ...
was drafted, and eight years before the present United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the Supremacy Clause, supreme law of the United States, United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, in 1789. Originally comprising seven ar ...
was ratified on June 21, 1788. Drafted by John Adams
John Adams (October 30, 1735 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, attorney, diplomat, writer, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the second president of the United States from 1797 to 1801. Befor ...
, the Massachusetts Constitution is currently the oldest functioning written constitution in continuous effect in the world. It has been amended 120 times, most recently in 2000.
Massachusetts politics since the second half of the 20th century have generally been dominated by the United States Democratic Party, Democratic Party, and the state has a reputation for being the most Modern liberalism in the United States, liberal state in the country. In 1974, Elaine Noble became List of the first LGBT holders of political offices, the first openly lesbian or gay candidate elected to a state legislature in US history. The state's Massachusetts's 12th congressional district, 12th congressional district elected the first openly gay member of the United States House of Representatives, Gerry Studds, in 1972 and in 2004, Massachusetts became the first state to allow same-sex marriage.[ In 2006, Massachusetts became the first state to approve a law that provided for nearly universal healthcare. Massachusetts has a pro-sanctuary city law.
In a 2020 study, Massachusetts was ranked as the 11th easiest state for citizens to vote in.
]
Government
 The Massachusetts government, Government of Massachusetts is divided into three branches: executive, legislative, and judicial. The governor of Massachusetts heads the executive branch, while legislative authority vests in a separate but coequal legislature. Meanwhile, judicial power is constitutionally guaranteed to the independent judicial branch.
The Massachusetts government, Government of Massachusetts is divided into three branches: executive, legislative, and judicial. The governor of Massachusetts heads the executive branch, while legislative authority vests in a separate but coequal legislature. Meanwhile, judicial power is constitutionally guaranteed to the independent judicial branch.
Executive branch
As chief executive, the governor is responsible for signing or vetoing legislation, filling judicial and agency appointments, granting pardons, preparing an annual budget, and commanding the Massachusetts National Guard.[ The current governor is Charlie Baker (politician), Charlie Baker,][ The council is charged by the state constitution with reviewing and confirming gubernatorial appointments and pardons, approving disbursements out of the state treasury, and certifying elections, among other duties.][
Aside from the governor and Executive Council, the executive branch also includes four independently elected constitutional officers: a Massachusetts Secretary of the Commonwealth, secretary of the commonwealth, an Massachusetts Attorney General, attorney general, a Treasurer and Receiver-General of Massachusetts, state treasurer, and a Massachusetts State Auditor, state auditor. The commonwealth's incumbent constitutional officers are respectively William F. Galvin, Maura Healey, Deb Goldberg and Suzanne Bump, all Massachusetts Democratic Party, Democrats. In accordance with state statute, the secretary of the commonwealth administers elections, regulates lobbyists and the securities industry, registers corporations, serves as register of deeds for the entire state, and preserves public records as keeper of the Seal of Massachusetts, state seal. Meanwhile, the attorney general provides legal services to state agencies, combats fraud and corruption, investigates and prosecutes crimes, and enforces consumer protection, environment, labor, and civil rights laws as Massachusetts chief lawyer and law enforcement officer. At the same time, the state treasurer manages the state's cash flow, debt, and investments as chief financial officer, whereas the state auditor conducts audits, investigations, and studies as chief audit executive in order to promote government accountability and transparency and improve state agency financial management, legal compliance, and performance.
]
Legislative branch
The Massachusetts House of Representatives and Massachusetts Senate comprise the legislature of Massachusetts, known as the Massachusetts General Court.[ The House consists of 160 members while the Senate has 40 members.][ Each branch consists of several committees.][ Members of both bodies are elected to two-year terms.
]
Judicial branch
The Massachusetts Supreme Judicial Court
The Massachusetts Supreme Judicial Court (SJC) is the court of last resort, highest court in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts. Although the claim is disputed by the Supreme Court of Pennsylvania, the SJC claims the di ...
(a chief justice and six associates) are appointed by the governor and confirmed by the Executive Council, as are all other judges in the state.
Federal representation
The Congressional delegation from Massachusetts is entirely Democratic Party (United States), Democratic. Currently, the United States Senate, Senators are Elizabeth Warren
Elizabeth Ann Warren ( née Herring; born June 22, 1949) is an American politician and former law professor who is the senior United States senator from Massachusetts, serving since 2013. A member of the Democratic Party and regarded as a ...
and Ed Markey while the United States House of Representatives, Representatives are Richard Neal (Massachusetts's 1st congressional district, 1st), Jim McGovern (congressman), Jim McGovern (Massachusetts's 2nd congressional district, 2nd), Lori Trahan (Massachusetts's 3rd congressional district, 3rd), Jake Auchincloss (Massachusetts's 4th congressional district, 4th), Katherine Clark (Massachusetts's 5th congressional district, 5th), Seth Moulton (Massachusetts's 6th congressional district, 6th), Ayanna Pressley (Massachusetts's 7th congressional district, 7th), Stephen Lynch (politician), Stephen Lynch (Massachusetts's 8th congressional district, 8th), and Bill Keating (politician), Bill Keating (Massachusetts's 9th congressional district, 9th).
In U.S. presidential elections since 2012, Massachusetts has been allotted 11 votes in the United States Electoral College, electoral college, out of a total of 538. Like most states, Massachusetts's electoral votes are granted in a winner-take-all system.
Politics
 Massachusetts has shifted from a previously Republican Party (United States), Republican-leaning state to one red states and blue states, largely dominated by Democratic Party (United States), Democrats; the United States Senate election in Massachusetts, 1952, 1952 victory of
Massachusetts has shifted from a previously Republican Party (United States), Republican-leaning state to one red states and blue states, largely dominated by Democratic Party (United States), Democrats; the United States Senate election in Massachusetts, 1952, 1952 victory of John F. Kennedy
John Fitzgerald Kennedy (May 29, 1917 – November 22, 1963), often referred to by his initials JFK and the nickname Jack, was an American politician who served as the 35th president of the United States from 1961 until his assassination i ...
over incumbent Senator Henry Cabot Lodge, Jr. is seen as a watershed moment in this transformation. His younger brother Ted Kennedy, Edward M. Kennedy held that seat until his death from a brain tumor in 2009. Since the 1950s, Massachusetts has gained a reputation as being a politically liberal state and is often used as an archetype of modern liberalism in the United States, modern liberalism, hence the phrase "Massachusetts liberal".
Massachusetts is one of the most Democratic states in the country. Democratic core concentrations are everywhere, except for a handful of Republican leaning towns in the Central and Southern parts of the state. Until recently, Republicans were dominant in the Western and Northern suburbs of Boston, however both areas heavily swung Democratic in the Trump era. The state as a whole has not given its Electoral College (United States), Electoral College votes to a Republican in a United States presidential election, presidential election since Ronald Reagan carried it in 1984 United States presidential election, 1984. Additionally, Massachusetts provided Reagan with his smallest margins of victory in both the 1980 United States presidential election, 1980 and 1984 elections. Massachusetts had been the only state to vote for Democrat George McGovern in the 1972 United States Presidential Election, 1972 Presidential Election. In 2020 United States presidential election in Massachusetts, 2020, Biden received 65.6% of the vote, the best performance in over 50 years for a Democrat.
Democrats have an absolute grip on the Massachusetts congressional delegation; there are no Republicans elected to serve at the federal level. Both Senators and all nine Representatives are Democrats; only one Republican (former Senator Scott Brown (politician), Scott Brown) has been elected to either house of Congress from Massachusetts since 1994. Massachusetts is the most populous state to be represented in the United States Congress entirely by a single party.
As of the 2018 elections, the Democratic Party holds a super-majority over the Republican Party in Bicameralism, both chambers of the Massachusetts General Court (state legislature). Out of the Massachusetts House of Representatives, state house's 160 seats, Democrats hold 127 seats (79%) compared to the Republican Party's 32 seats (20%), an Susannah Whipps, independent sits in the remaining one, and 37 out of the 40 seats in the Massachusetts state senate, state senate (92.5%) belong to the Democratic Party compared to the Republican Party's three seats (7.5%). Both houses of the legislature have had Democratic majorities since the 1950s.
Despite the state's Democratic-leaning tendency, Massachusetts has generally elected Republicans as governor of Massachusetts, Governor: only one Democrat (Deval Patrick) has served as governor since 1991, and among gubernatorial election results from 2002 to 2018, Republican nominees garnered 48.4% of the vote compared to 45.7% for Democratic nominees.
Cities, towns, and counties
There are List of municipalities in Massachusetts, 50 cities and 301 towns in Massachusetts, grouped into List of Massachusetts counties, 14 counties.Greater Boston
Greater Boston is the metropolitan region of New England encompassing the municipality of Boston (the capital of the U.S. state of Massachusetts and the most populous city in New England) and its surrounding areas. The region forms the northern ar ...
, with a population of 4,873,019, is the 11th largest metropolitan area in the nation. Other cities with a population over 100,000 include Worcester, Massachusetts, Worcester, Springfield
Springfield may refer to:
* Springfield (toponym), the place name in general
Places and locations Australia
* Springfield, New South Wales (Central Coast)
* Springfield, New South Wales (Snowy Monaro Regional Council)
* Springfield, Queenslan ...
, Lowell, and Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge bec ...
. Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west.
Plymouth ...
is the largest municipality in the state by land area, followed by Middleborough, Massachusetts, Middleborough.New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
states, features the local governmental structure known as New England town, the New England town. In this structure, incorporated towns—as opposed to townships or counties—hold many of the responsibilities and powers of local government. Most of the county governments were abolished by the state of Massachusetts beginning in 1997 including Middlesex County, Massachusetts, Middlesex County, the largest county in the state by population. The voters of these now-defunct counties elect only Sheriffs and Registers of Deeds, who are part of the state government. Other counties have been reorganized, and a few still retain county councils.
Arts, culture, and recreation
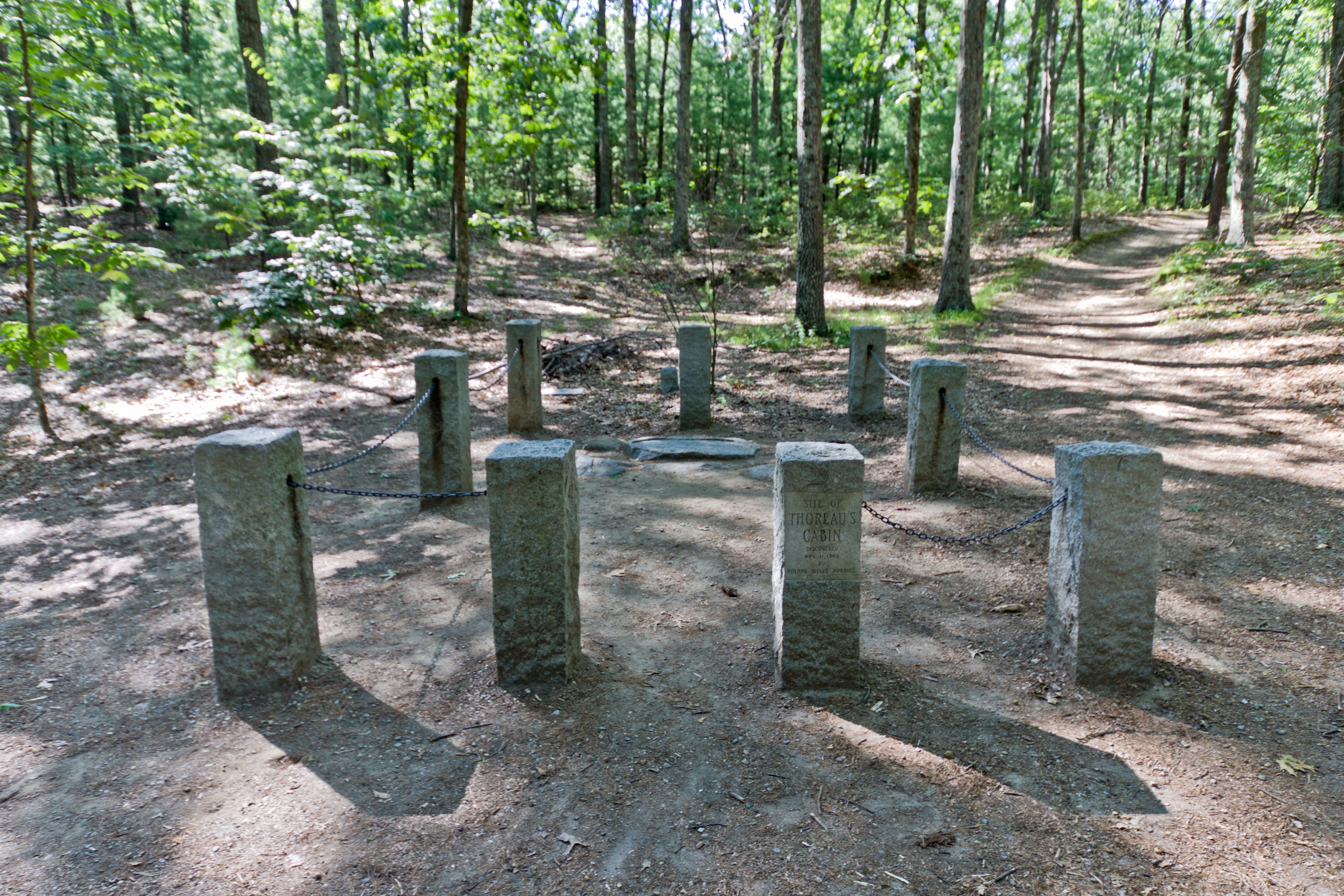
 Massachusetts has contributed to American arts and culture. Drawing from its Native Americans in the United States, Native American and
Massachusetts has contributed to American arts and culture. Drawing from its Native Americans in the United States, Native American and Yankee
The term ''Yankee'' and its contracted form ''Yank'' have several interrelated meanings, all referring to people from the United States. Its various senses depend on the context, and may refer to New Englanders, residents of the Northern United St ...
roots, along with later immigrant groups, Massachusetts has produced several writers, artists, and musicians. Some major museums and important historical sites are also located there, and events and festivals throughout the year celebrate the state's history and heritage.
Massachusetts was an early center of the Transcendentalism, Transcendentalist movement, which emphasized intuition, emotion, human individuality and a deeper connection with nature. Ralph Waldo Emerson
Ralph Waldo Emerson (May 25, 1803April 27, 1882), who went by his middle name Waldo, was an American essayist, lecturer, philosopher, abolitionist, and poet who led the transcendentalist movement of the mid-19th century. He was seen as a champ ...
, who was born in Boston but spent much of his later life in Concord, Massachusetts, Concord, largely created the philosophy with his 1836 work Nature (essay), ''Nature'', and continued to be a key figure in the movement for the remainder of his life. Emerson's friend, Henry David Thoreau
Henry David Thoreau (July 12, 1817May 6, 1862) was an American naturalist, essayist, poet, and philosopher. A leading Transcendentalism, transcendentalist, he is best known for his book ''Walden'', a reflection upon simple living in natural su ...
, who was also involved in Transcendentalism, recorded his year spent alone in a small cabin at nearby Walden Pond in the 1854 work ''Walden; or, Life in the Woods''.
Other famous authors and poets born or strongly associated with Massachusetts include Anne Bradstreet, Nathaniel Hawthorne, Louisa May Alcott, Robert Frost, Emily Dickinson, Henry Wadsworth Longfellow, Edith Wharton, e.e. cummings, Herman Melville, W.E.B. Du Bois, Sylvia Plath, Elizabeth Bishop, John Updike, Anne Sexton, H.P. Lovecraft, Edgar Allan Poe, Helen Hunt Jackson, Khalil Gibran, Mary Higgins Clark, Amelia Atwater-Rhodes, Jack Kerouac and Dr. Seuss, Theodor Seuss Geisel, better known as "Dr. Seuss".[ many of the latter's works are on display at the Norman Rockwell Museum in Stockbridge, Massachusetts, Stockbridge.
Massachusetts is also an important center for the performing arts. Both the Boston Symphony Orchestra and Boston Pops Orchestra are based in Massachusetts.][ and the Lenox, Massachusetts, Lenox-based Shakespeare & Company (Massachusetts), Shakespeare & Company. In addition to classical and folk music, Massachusetts has produced musicians and bands spanning a number of contemporary genres, such as the classic rock band Aerosmith, the proto-punk band The Modern Lovers, the New wave music, new wave band The Cars, and the alternative rock band Pixies (band), Pixies. The state has also been the birthplace of the rock bands Staind, Godsmack, and Highly Suspect, since these bands all were formed in Massachusetts cities such Springfield (Massachusetts), Springfield, Lawrence, Massachusetts, Lawrence, and Cape Cod respectively. Film events in the state include the Boston Film Festival, the Boston International Film Festival, and a number of smaller film festivals in various cities throughout Massachusetts.
] Massachusetts is home to a large number of museums and historical sites. The Museum of Fine Arts, Boston, the Institute of Contemporary Art, Boston, and the DeCordova Museum, DeCordova contemporary art and sculpture museum in Lincoln, Massachusetts, Lincoln are all located within Massachusetts, and the Maria Mitchell Association in
Massachusetts is home to a large number of museums and historical sites. The Museum of Fine Arts, Boston, the Institute of Contemporary Art, Boston, and the DeCordova Museum, DeCordova contemporary art and sculpture museum in Lincoln, Massachusetts, Lincoln are all located within Massachusetts, and the Maria Mitchell Association in Nantucket
Nantucket () is an island about south from Cape Cod. Together with the small islands of Tuckernuck and Muskeget, it constitutes the Town and County of Nantucket, a combined county/town government that is part of the U.S. state of Massachuse ...
includes several observatories, museums, and an aquarium. Historically themed museums and sites such as the Springfield Armory National Historic Site in Springfield
Springfield may refer to:
* Springfield (toponym), the place name in general
Places and locations Australia
* Springfield, New South Wales (Central Coast)
* Springfield, New South Wales (Snowy Monaro Regional Council)
* Springfield, Queenslan ...
,[ Boston's Freedom Trail and nearby Minute Man National Historical Park, both of which preserve a number of sites important during the ]American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolut ...
,[ the Lowell National Historical Park, which focuses on some of the earliest mills and canals of the industrial revolution in the US,][ the Black Heritage Trail in Boston, which includes important African-American and abolitionist sites in Boston, and the New Bedford Whaling National Historical Park][ all showcase various periods of Massachusetts's history.
Plimoth Plantation and Old Sturbridge Village are two open-air museum, open-air or "living" museums in Massachusetts, recreating life as it was in the 17th and early 19th centuries, respectively.
Boston's annual St. Patrick's Day parade and "Harborfest", a week-long Fourth of July celebration featuring a fireworks display and concert by the Boston Pops as well as a turnaround cruise in Boston Harbor by the USS Constitution, USS ''Constitution'', are popular events. The New England Summer Nationals, an auto show in Worcester, draws tens of thousands of attendees every year. The ]Boston Marathon
The Boston Marathon is an annual marathon race hosted by several cities and towns in greater Boston in eastern Massachusetts, United States. It is traditionally held on Patriots' Day, the third Monday of April. Begun in 1897, the event was i ...
is also a popular event in the state drawing more than 30,000 runners and tens of thousands of spectators annually.
Long-distance hiking trails in Massachusetts include the Appalachian Trail, the New England National Scenic Trail, the Metacomet-Monadnock Trail, the Midstate Trail (Massachusetts), Midstate Trail, and the Bay Circuit Trail. Other outdoor recreational activities in Massachusetts include sailing and yachting, freshwater and deep-sea fishing, whale watching, downhill and cross-country skiing, and hunting.
Massachusetts is one of the states with the largest percentage of Catholics. It has many sanctuaries such as the National Shrine of The Divine Mercy (Stockbridge, Massachusetts).
Media
There are two major television media markets located in Massachusetts. The Boston/Manchester market is the fifth-largest in the United States. The other market surrounds the Springfield area. WGBH-TV in Boston is a major public television station and produces national programs such as Nova (American TV series), ''Nova'', Frontline (U.S. TV series), ''Frontline'', and ''American Experience''.
''The Boston Globe'', ''Boston Herald'', ''Springfield Republican'', and the ''Worcester Telegram & Gazette'' are Massachusetts's largest daily newspapers. In addition, there are many community dailies and weeklies. The Associated Press maintains a bureau in Boston, and local news wire the State House News Service feeds coverage of state government to other Massachusetts media outlets. There are a number of major AM broadcasting, AM and FM broadcasting, FM stations which serve Massachusetts, along with many more regional and community-based stations. Some colleges and universities also operate campus television and radio stations, and print their own newspapers.
Health
 Massachusetts generally ranks highly among states in most health and disease prevention categories. In 2015, the UnitedHealth Group, United Health Foundation ranked the state as third-healthiest overall. Massachusetts has the most doctors per 100,000 residents (435.38), the second-lowest infant mortality rate (3.8), and the lowest percentage of uninsured residents (children as well as the total population). According to ''Business Insider'', commonwealth residents have an average life expectancy of 80.41 years, the fifth-longest in the country. 36.1% of the population is overweight and 24.4% is obese,
Massachusetts generally ranks highly among states in most health and disease prevention categories. In 2015, the UnitedHealth Group, United Health Foundation ranked the state as third-healthiest overall. Massachusetts has the most doctors per 100,000 residents (435.38), the second-lowest infant mortality rate (3.8), and the lowest percentage of uninsured residents (children as well as the total population). According to ''Business Insider'', commonwealth residents have an average life expectancy of 80.41 years, the fifth-longest in the country. 36.1% of the population is overweight and 24.4% is obese,[ Massachusetts also ranks above average in the prevalence of binge drinking, which is the 20th-highest in the country.
The nation's first Marine Hospital Service, Marine Hospital was erected by federal order in Boston in 1799. There are currently a total of 143 hospitals in the state. According to 2015 rankings by ''U.S. News & World Report'', Massachusetts General Hospital is ranked in the top three in two health care specialties. Massachusetts General was founded in 1811 and serves as the largest teaching hospital for nearby ]Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher le ...
.
The state of Massachusetts is a center for medical education and research including Harvard's Brigham and Women's Hospital, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, and Dana–Farber Cancer Institute as well as the New England Baptist Hospital, Tufts Medical Center, and Boston Medical Center which is the primary teaching hospital for Boston University. The University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School is located in Worcester, Massachusetts, Worcester. The Massachusetts College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences has two of its three campuses in Boston and Worcester.
Sports
 Massachusetts is home to five major league professional sports teams: seventeen-time NBA Finals, NBA Champions Boston Celtics, nine-time World Series winners Boston Red Sox, six-time Stanley Cup winners Boston Bruins, six-time Super Bowl winners New England Patriots, and Major League Soccer team New England Revolution.
In the late 19th century, the Olympics, Olympic sports of basketball
Massachusetts is home to five major league professional sports teams: seventeen-time NBA Finals, NBA Champions Boston Celtics, nine-time World Series winners Boston Red Sox, six-time Stanley Cup winners Boston Bruins, six-time Super Bowl winners New England Patriots, and Major League Soccer team New England Revolution.
In the late 19th century, the Olympics, Olympic sports of basketball[ and volleyball][ were invented in the Western Massachusetts cities of ]Springfield
Springfield may refer to:
* Springfield (toponym), the place name in general
Places and locations Australia
* Springfield, New South Wales (Central Coast)
* Springfield, New South Wales (Snowy Monaro Regional Council)
* Springfield, Queenslan ...
[ and Holyoke,][ respectively. The Basketball Hall of Fame is a major tourist destination in the City of Springfield and the Volleyball Hall of Fame is located in Holyoke.][ The American Hockey League (AHL), the NHL's development league, is headquartered in Springfield.
Several universities in Massachusetts are notable for their collegiate athletics. The state is home to two NCAA Division I Football Bowl Subdivision, DivisionI FBS teams, Boston College of the Atlantic Coast Conference, and FBS NCAA Division I FBS independent schools, Independent University of Massachusetts Amherst, University of Massachusetts at Amherst. Football Championship Subdivision, FCS play includes ]Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher le ...
, which competes in the famed Ivy League, and College of the Holy Cross of the Patriot League. Boston University, Northeastern University (Boston, Massachusetts), Northeastern University, University of Massachusetts Lowell, UMASS Lowell, and Merrimack College also participate in DivisionI athletics. Many other Massachusetts colleges compete in lower divisions such as Division III (NCAA), DivisionIII, where MIT, Tufts University, Amherst College, Williams College, and others field competitive teams.
Massachusetts is also the home of rowing events such as the Eastern Sprints on Lake Quinsigamond and the Head of the Charles Regatta. A number of major golf events have taken place in Massachusetts, including nine U.S. Open (golf), U.S. Opens and two Ryder Cups. Massachusetts is also the home of the Cape Cod Baseball League, and Premier Lacrosse League team Cannons Lacrosse Club.
Massachusetts has produced several successful Olympians including Thomas Burke (athlete), Thomas Burke, James Brendan Connolly, James Connolly, and John Thomas (athlete), John Thomas (Track and field at the Summer Olympics, track & field); Butch Johnson (Archery at the Summer Olympics, archery); Nancy Kerrigan (Figure skating at the Olympic Games, figure skating); Todd Richards (snowboarder), Todd Richards (Snowboarding at the Winter Olympics, snowboarding); Albina Osipowich (Swimming at the Summer Olympics, swimming); Aly Raisman (Gymnastics at the Summer Olympics, gymnastics); Patrick Ewing (Basketball at the Summer Olympics, basketball); as well as Jim Craig (ice hockey), Jim Craig, Mike Eruzione, Bill Cleary (ice hockey), Bill Cleary, Keith Tkachuk (Ice hockey at the Olympic Games, ice hockey).
See also
* Index of Massachusetts-related articles
* Outline of Massachusetts
* ''''
Notes
References
Bibliography
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
Overviews and surveys
* Hall, Donald. ed. ''The Encyclopedia of New England'' (2005)
* Works Progress Administration. ''Guide to Massachusetts'' (1939)
Secondary sources
* Abrams, Richard M. ''Conservatism in a Progressive Era: Massachusetts Politics, 1900–1912'' (1964)
* Adams, James Truslow. ''Revolutionary New England, 1691–1776'' (1923)
* Adams, James Truslow. ''New England in the Republic, 1776–1850'' (1926)
* Andrews, Charles M. ''The Fathers of New England: A Chronicle of the Puritan Commonwealths'' (1919), short survey
* Conforti, Joseph A. ''Imagining New England: Explorations of Regional Identity from the Pilgrims to the Mid-Twentieth Century'' (2001)
* Cumbler, John T. ''Reasonable Use: The People, the Environment, and the State, New England, 1790–1930'' (1930), environmental history
* Fischer, David Hackett. ''Paul Revere's Ride'' (1994), 1775 in depth
* Flagg, Charles Allcott
''A Guide to Massachusetts local history''
Salem : Salem Press Company, 1907.
* Green, James R., William F. Hartford, and Tom Juravich. ''Commonwealth of Toil: Chapters in the History of Massachusetts Workers and Their Unions'' (1996)
* Huthmacher, J. Joseph. ''Massachusetts People and Politics, 1919–1933'' (1958)
* Labaree, Benjamin Woods. ''Colonial Massachusetts: A History'' (1979)
* Morison, Samuel Eliot. ''The Maritime History of Massachusetts, 1783–1860'' (1921)
* Peirce, Neal R. ''The New England States: People, Politics, and Power in the Six New England States'' (1976), 1960–75 era
* Porter, Susan L. ''Women of the Commonwealth: Work, Family, and Social Change in Nineteenth-Century Massachusetts'' (1996)
* Sletcher, Michael. ''New England'' (2004).
* Starkey, Marion L. ''The Devil in Massachusetts'' (1949), Salem witches
* Tager, Jack, and John W. Ifkovic, eds. ''Massachusetts in the Gilded Age: Selected Essays'' (1985), ethnic groups
* Zimmerman, Joseph F.
The New England Town Meeting: Democracy in Action
' (1999)
External links
*
Massachusetts Office of Travel and Tourism
from the Library of Congress
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Massachusetts, Commonwealth of
Massachusetts,
1788 establishments in the United States
Contiguous United States
New England states
Northeastern United States
States and territories established in 1788
States of the East Coast of the United States
States of the United States
 The first English colonizers in Massachusetts, the
The first English colonizers in Massachusetts, the  Massachusetts was a center of the movement for independence from
Massachusetts was a center of the movement for independence from  During the 19th century, Massachusetts became a national leader in the American
During the 19th century, Massachusetts became a national leader in the American  The
The  Two pressure cooker bombs exploded near the finish line of the
Two pressure cooker bombs exploded near the finish line of the  Massachusetts is the 7th-smallest state in the United States. It is located in the
Massachusetts is the 7th-smallest state in the United States. It is located in the  At the 2020 United States census, 2020 U.S. census, Massachusetts had a population of over 7 million, a 7.4% increase since the 2010 United States Census, 2010 United States census. As of 2015, Massachusetts was estimated to be the List of states and territories of the United States by population density, third-most densely populated U.S. state, with 871.0 people per square mile, behind New Jersey and
At the 2020 United States census, 2020 U.S. census, Massachusetts had a population of over 7 million, a 7.4% increase since the 2010 United States Census, 2010 United States census. As of 2015, Massachusetts was estimated to be the List of states and territories of the United States by population density, third-most densely populated U.S. state, with 871.0 people per square mile, behind New Jersey and  The state's most populous ethnic group, non-Hispanic white, has declined from 95.4% in 1970 to 67.6% in 2020. As of 2011, non-Hispanic whites were involved in 63.6% of all the births, while 36.4% of the population of Massachusetts younger than age1 was minorities (at least one parent who was not non-Hispanic white). One major reason for this is that non-Hispanic whites in Massachusetts recorded a total fertility rate of 1.36 in 2017, the second-lowest in the country after neighboring Rhode Island.
As late as 1795, the population of Massachusetts was nearly 95% of English ancestry. During the early and mid-19th century, immigrant groups began arriving in Massachusetts in large numbers; first from Ireland in the 1840s; today the Irish and part-Irish are the largest ancestry group in the state at nearly 25% of the total population. Others arrived later from Quebec as well as places in Europe such as Italy, Portugal, and Poland. In the early 20th century, a number of Great Migration (African American), African Americans migrated to Massachusetts, although in somewhat fewer numbers than many other Northern states. Later in the 20th century, immigration from Latin America increased considerably. More than 156,000 Chinese Americans in Boston, Chinese Americans made their home in Massachusetts in 2014, and Boston hosts a growing Chinatown, Boston, Chinatown accommodating heavily traveled Chinatown bus lines, Chinese-owned bus lines to and from Chinatown, Manhattan in New York City. Massachusetts also has large Dominican American, Dominican, Puerto Rican American, Puerto Rican, Haitian Americans, Haitian, Cape Verdean American, Cape Verdean and Brazilian American, Brazilian populations. Boston's South End, Boston, South End and Jamaica Plain are both gay villages, as is nearby Provincetown, Massachusetts on Cape Cod.
The state's most populous ethnic group, non-Hispanic white, has declined from 95.4% in 1970 to 67.6% in 2020. As of 2011, non-Hispanic whites were involved in 63.6% of all the births, while 36.4% of the population of Massachusetts younger than age1 was minorities (at least one parent who was not non-Hispanic white). One major reason for this is that non-Hispanic whites in Massachusetts recorded a total fertility rate of 1.36 in 2017, the second-lowest in the country after neighboring Rhode Island.
As late as 1795, the population of Massachusetts was nearly 95% of English ancestry. During the early and mid-19th century, immigrant groups began arriving in Massachusetts in large numbers; first from Ireland in the 1840s; today the Irish and part-Irish are the largest ancestry group in the state at nearly 25% of the total population. Others arrived later from Quebec as well as places in Europe such as Italy, Portugal, and Poland. In the early 20th century, a number of Great Migration (African American), African Americans migrated to Massachusetts, although in somewhat fewer numbers than many other Northern states. Later in the 20th century, immigration from Latin America increased considerably. More than 156,000 Chinese Americans in Boston, Chinese Americans made their home in Massachusetts in 2014, and Boston hosts a growing Chinatown, Boston, Chinatown accommodating heavily traveled Chinatown bus lines, Chinese-owned bus lines to and from Chinatown, Manhattan in New York City. Massachusetts also has large Dominican American, Dominican, Puerto Rican American, Puerto Rican, Haitian Americans, Haitian, Cape Verdean American, Cape Verdean and Brazilian American, Brazilian populations. Boston's South End, Boston, South End and Jamaica Plain are both gay villages, as is nearby Provincetown, Massachusetts on Cape Cod.
 The largest ancestry group in Massachusetts are the Irish Americans, Irish (22.5% of the population), who live in significant numbers throughout the state but form more than 40% of the population along the South Shore in Norfolk and Plymouth counties (in both counties overall, Irish-Americans comprise more than 30% of the population). Italian Americans, Italians form the second-largest ethnic group in the state (13.5%), but form a plurality in some suburbs north of Boston and in a few towns in the Berkshires. English Americans, the third-largest (11.4%) group, form a plurality in some western towns. French Americans, French and French Canadians also form a significant part (10.7%), with sizable populations in Bristol, Hampden, and Worcester Counties, along with Middlesex county especially concentrated in the areas surrounding Lowell and Lawrence. Lowell is home to the second-largest Cambodian Americans, Cambodian community of the nation. Massachusetts is home to a small community of Greek Americans as well, which according to the American Community Survey there are 83,701 of them scattered along the state (1.2% of the total state population). There are also List of American Indian Reservations in Massachusetts, several populations of Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans in Massachusetts. The
The largest ancestry group in Massachusetts are the Irish Americans, Irish (22.5% of the population), who live in significant numbers throughout the state but form more than 40% of the population along the South Shore in Norfolk and Plymouth counties (in both counties overall, Irish-Americans comprise more than 30% of the population). Italian Americans, Italians form the second-largest ethnic group in the state (13.5%), but form a plurality in some suburbs north of Boston and in a few towns in the Berkshires. English Americans, the third-largest (11.4%) group, form a plurality in some western towns. French Americans, French and French Canadians also form a significant part (10.7%), with sizable populations in Bristol, Hampden, and Worcester Counties, along with Middlesex county especially concentrated in the areas surrounding Lowell and Lawrence. Lowell is home to the second-largest Cambodian Americans, Cambodian community of the nation. Massachusetts is home to a small community of Greek Americans as well, which according to the American Community Survey there are 83,701 of them scattered along the state (1.2% of the total state population). There are also List of American Indian Reservations in Massachusetts, several populations of Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans in Massachusetts. The  Massachusetts was founded and settled by Brownist
Massachusetts was founded and settled by Brownist  In 2018, Massachusetts's overall educational system was ranked the top among all fifty U.S. states by ''U.S. News & World Report''. Massachusetts was the first state in North America to require municipalities to appoint a teacher or establish a grammar school with the passage of the Massachusetts School Laws, Massachusetts Education Law of 1647, and 19th century reforms pushed by
In 2018, Massachusetts's overall educational system was ranked the top among all fifty U.S. states by ''U.S. News & World Report''. Massachusetts was the first state in North America to require municipalities to appoint a teacher or establish a grammar school with the passage of the Massachusetts School Laws, Massachusetts Education Law of 1647, and 19th century reforms pushed by  While manufacturing comprised less than 10% of Massachusetts's gross state product in 2016, the Commonwealth ranked 16th in the nation in total manufacturing output in the United States. This includes a diverse array of manufactured goods such as medical devices, paper goods, specialty chemicals and plastics, telecommunications and electronics equipment, and machined components.
The more than 33,000 nonprofits in Massachusetts employ one-sixth of the state's workforce. In 2007, Governor Deval Patrick signed into law a state holiday, Nonprofit Awareness Day.
In February 2017, ''U.S. News & World Report'' ranked Massachusetts the best state in the United States based upon 60 Performance metric, metrics including healthcare, education, crime, infrastructure, opportunity, economy, and government. The Bay State ranked number one in education, number two in healthcare, and number five in the handling of the economy.
While manufacturing comprised less than 10% of Massachusetts's gross state product in 2016, the Commonwealth ranked 16th in the nation in total manufacturing output in the United States. This includes a diverse array of manufactured goods such as medical devices, paper goods, specialty chemicals and plastics, telecommunications and electronics equipment, and machined components.
The more than 33,000 nonprofits in Massachusetts employ one-sixth of the state's workforce. In 2007, Governor Deval Patrick signed into law a state holiday, Nonprofit Awareness Day.
In February 2017, ''U.S. News & World Report'' ranked Massachusetts the best state in the United States based upon 60 Performance metric, metrics including healthcare, education, crime, infrastructure, opportunity, economy, and government. The Bay State ranked number one in education, number two in healthcare, and number five in the handling of the economy.
 Massachusetts has 10 regional metropolitan planning organizations and three non-metropolitan planning organizations covering the remainder of the state; statewide planning is handled by the Massachusetts Department of Transportation. Transportation is the single largest source of greenhouse gas emissions by economic sector in Massachusetts.
Massachusetts has 10 regional metropolitan planning organizations and three non-metropolitan planning organizations covering the remainder of the state; statewide planning is handled by the Massachusetts Department of Transportation. Transportation is the single largest source of greenhouse gas emissions by economic sector in Massachusetts.
 Logan International Airport, Boston Logan International Airport served 33.5million passengers in 2015 (up from 31.6million in 2014) through 103 Gate (airport), gates. Logan, Hanscom Field in Bedford, Massachusetts, Bedford, and Worcester Regional Airport are operated by Massport, an independent state transportation agency. Massachusetts has 39 public-use airfields and more than 200 private landing spots. Some airports receive funding from the Aeronautics Division of the Massachusetts Department of Transportation and the Federal Aviation Administration; the FAA is also the primary regulator of Massachusetts air travel.
Logan International Airport, Boston Logan International Airport served 33.5million passengers in 2015 (up from 31.6million in 2014) through 103 Gate (airport), gates. Logan, Hanscom Field in Bedford, Massachusetts, Bedford, and Worcester Regional Airport are operated by Massport, an independent state transportation agency. Massachusetts has 39 public-use airfields and more than 200 private landing spots. Some airports receive funding from the Aeronautics Division of the Massachusetts Department of Transportation and the Federal Aviation Administration; the FAA is also the primary regulator of Massachusetts air travel.
 There are a total of of Interstate highway, interstates and other highways in Massachusetts. Massachusetts Turnpike, Interstate90 (I-90, also known as the Massachusetts Turnpike), is the longest interstate in Massachusetts. The route travels generally west to east, entering Massachusetts at the New York state line in the town of West Stockbridge, Massachusetts, West Stockbridge, and passes just north of
There are a total of of Interstate highway, interstates and other highways in Massachusetts. Massachusetts Turnpike, Interstate90 (I-90, also known as the Massachusetts Turnpike), is the longest interstate in Massachusetts. The route travels generally west to east, entering Massachusetts at the New York state line in the town of West Stockbridge, Massachusetts, West Stockbridge, and passes just north of  Massachusetts has a long political history; earlier political structures included the Mayflower Compact of 1620, the separate Massachusetts Bay Colony, Massachusetts Bay and Plymouth Colony, Plymouth colonies, and the combined colonial Province of Massachusetts. The
Massachusetts has a long political history; earlier political structures included the Mayflower Compact of 1620, the separate Massachusetts Bay Colony, Massachusetts Bay and Plymouth Colony, Plymouth colonies, and the combined colonial Province of Massachusetts. The  The Massachusetts government, Government of Massachusetts is divided into three branches: executive, legislative, and judicial. The governor of Massachusetts heads the executive branch, while legislative authority vests in a separate but coequal legislature. Meanwhile, judicial power is constitutionally guaranteed to the independent judicial branch.
The Massachusetts government, Government of Massachusetts is divided into three branches: executive, legislative, and judicial. The governor of Massachusetts heads the executive branch, while legislative authority vests in a separate but coequal legislature. Meanwhile, judicial power is constitutionally guaranteed to the independent judicial branch.
 Massachusetts has shifted from a previously Republican Party (United States), Republican-leaning state to one red states and blue states, largely dominated by Democratic Party (United States), Democrats; the United States Senate election in Massachusetts, 1952, 1952 victory of
Massachusetts has shifted from a previously Republican Party (United States), Republican-leaning state to one red states and blue states, largely dominated by Democratic Party (United States), Democrats; the United States Senate election in Massachusetts, 1952, 1952 victory of  Massachusetts has contributed to American arts and culture. Drawing from its Native Americans in the United States, Native American and
Massachusetts has contributed to American arts and culture. Drawing from its Native Americans in the United States, Native American and  Massachusetts is home to a large number of museums and historical sites. The Museum of Fine Arts, Boston, the Institute of Contemporary Art, Boston, and the DeCordova Museum, DeCordova contemporary art and sculpture museum in Lincoln, Massachusetts, Lincoln are all located within Massachusetts, and the Maria Mitchell Association in
Massachusetts is home to a large number of museums and historical sites. The Museum of Fine Arts, Boston, the Institute of Contemporary Art, Boston, and the DeCordova Museum, DeCordova contemporary art and sculpture museum in Lincoln, Massachusetts, Lincoln are all located within Massachusetts, and the Maria Mitchell Association in  Massachusetts generally ranks highly among states in most health and disease prevention categories. In 2015, the UnitedHealth Group, United Health Foundation ranked the state as third-healthiest overall. Massachusetts has the most doctors per 100,000 residents (435.38), the second-lowest infant mortality rate (3.8), and the lowest percentage of uninsured residents (children as well as the total population). According to ''Business Insider'', commonwealth residents have an average life expectancy of 80.41 years, the fifth-longest in the country. 36.1% of the population is overweight and 24.4% is obese, and Massachusetts ranks sixth-highest in the percentage of residents who are considered neither obese nor overweight (39.5%). Massachusetts also ranks above average in the prevalence of binge drinking, which is the 20th-highest in the country.
The nation's first Marine Hospital Service, Marine Hospital was erected by federal order in Boston in 1799. There are currently a total of 143 hospitals in the state. According to 2015 rankings by ''U.S. News & World Report'', Massachusetts General Hospital is ranked in the top three in two health care specialties. Massachusetts General was founded in 1811 and serves as the largest teaching hospital for nearby
Massachusetts generally ranks highly among states in most health and disease prevention categories. In 2015, the UnitedHealth Group, United Health Foundation ranked the state as third-healthiest overall. Massachusetts has the most doctors per 100,000 residents (435.38), the second-lowest infant mortality rate (3.8), and the lowest percentage of uninsured residents (children as well as the total population). According to ''Business Insider'', commonwealth residents have an average life expectancy of 80.41 years, the fifth-longest in the country. 36.1% of the population is overweight and 24.4% is obese, and Massachusetts ranks sixth-highest in the percentage of residents who are considered neither obese nor overweight (39.5%). Massachusetts also ranks above average in the prevalence of binge drinking, which is the 20th-highest in the country.
The nation's first Marine Hospital Service, Marine Hospital was erected by federal order in Boston in 1799. There are currently a total of 143 hospitals in the state. According to 2015 rankings by ''U.S. News & World Report'', Massachusetts General Hospital is ranked in the top three in two health care specialties. Massachusetts General was founded in 1811 and serves as the largest teaching hospital for nearby  Massachusetts is home to five major league professional sports teams: seventeen-time NBA Finals, NBA Champions Boston Celtics, nine-time World Series winners Boston Red Sox, six-time Stanley Cup winners Boston Bruins, six-time Super Bowl winners New England Patriots, and Major League Soccer team New England Revolution.
In the late 19th century, the Olympics, Olympic sports of basketball and volleyball were invented in the Western Massachusetts cities of
Massachusetts is home to five major league professional sports teams: seventeen-time NBA Finals, NBA Champions Boston Celtics, nine-time World Series winners Boston Red Sox, six-time Stanley Cup winners Boston Bruins, six-time Super Bowl winners New England Patriots, and Major League Soccer team New England Revolution.
In the late 19th century, the Olympics, Olympic sports of basketball and volleyball were invented in the Western Massachusetts cities of